GRADE
10
Science
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Biology: Tissues, Organs, and Systems
Cells
Definition of Life, Cell Theory
Which of the following is not one of the main ideas of cell theory?
Solution
All cells cannot carry out the same functions
Cell Definitions
An organism can be made of only one cell.
Solution
E.g.) Amoeba or Paramecium.
All living organisms are made of
Solution
All living organisms are made of cells. Single-celled organisms do not contain organ systems, organs, or tissues.
Cells and Differences
The main difference below, between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is,
Solution
Eukaryotes have nuclei, prokaryotes do not.
The main difference between plant and animal cells is the presence of a
Solution
The main difference between plant and animal cells is the presence of a cell wall. Also animal cells don't have chloroplasts.
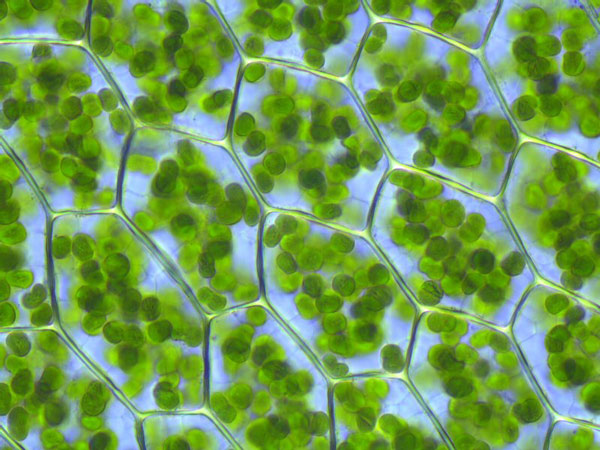
Explain two organelle differences you would observe comparing onion and skin cells under a microscope.
Solution
Only onion cells would have cell wall, and chloroplast...
Cellular respiration occurs in both plant and animal cells, while photosynthesis can only occur in plant cells. Solution
 |
Cell Functions
Which of the following is responsible for cellular transport throughout the cell?
Solution
Cellular transport throughout the cell occurs with a process called diffusion. Diffusion is the transport of molecules across a gradient of high concentration towards lower concentration in a fluid.
In which organelle does the following reaction take place?
Solution
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
This manufacture of energy from sugar occurs in the mitochondria. The powerhouse of cells.
Cell Division
The phase of the cell cycle in which genetic material is copied is
Solution

Interphase: DNA is copied and the cell grows to prepare for cellular division.
Cell Division
The phase of the cell cycle in which chromosomes are first visible under microscope is
Solution
Prophase: the chromosomes condense into visible forms under a microscope.
The final stage of cell division is called telophase
Solution
The final phase is cytokinesis, which the cell is split into two daughter cells.
The longest cellular phase is interphase.
Solution
(Technically this is not the longest phase of mitosis because interphase is not considered a part of mitosis-PMAT).
Cell Division
What occurs during anaphase? Solution
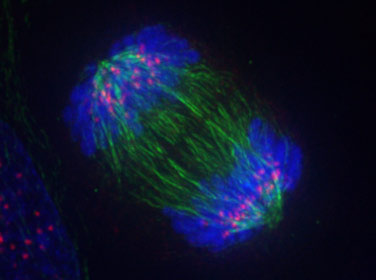 |
- The nuclear membrane dissolves during prophase.
- Chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell in metaphase.
- The chromatids separate to opposite sides of the cell in anaphase.
- The chromatids rearrange at opposite ends of the cell in telophase and nuclear membrane forms.
- (The cytoplasm divides in cytokinesis)
Cell Division
Draw the 6 stages of mitosis.
Solution
I.-P.M.A.T.-C.
- The cell is at rest in interphase
- The nuclear membrane dissolves during prophase.
- Chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell in metaphase.
- The chromatids separate to opposite sides of the cell in anaphase.
- The chromatids rearrange at opposite ends of the cell in telophase and nuclear membrane forms.
- (The cytoplasm divides in cytokinesis)
Draw the following stages (not shown): interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
- The cell is at rest in interphase
- The nuclear membrane dissolves during prophase.
- Chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell in metaphase.
- The chromatids separate to opposite sides of the cell in anaphase.
- The chromatids rearrange at opposite ends of the cell in telophase and nuclear membrane forms.
- (The cytoplasm divides in cytokinesis)
Cell Division: Cancer
Cancer cells that grow in a confined region and do not spread, are called
Solution
Benign.
Cancer is defined when cells grow too large.
Solution
Cancer is when cells grow uncontrollably, at an increased rate of cell division. (Growing too large is a result/indication)
Cell Division: Cancer
Describe how cell division is involved in cancer and state at least three causes of cancer. [4]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
During cell division DNA is replicated. If a part of the DNA that is responsible for controlling cell division gets mutated, the resulting cells could grow and divide uncontrollably at an increased rate - this is cancer. Some things that can cause cancer: smoking, radiation, or hereditary gene mutations. (Answers may vary)
Cell Systems
Organization of Cell Systems
Rank the following levels of organization in organisms from the smallest level to the highest (from top to bottom).
Solution
Organ
Cell
Organism
Organ System
Tissue
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System → Organism.
Tissue Definition
Tissue is:
Solution
Tissue: cells that perform a similar function.
Tissues
Which type of tissue is described as long, thin cells that conduct electrical impulses?
Solution
Nerve Tissue.
Tissues
The heart is an example of what type of tissue?
Solution
Muscle Tissue
Which tissue lines the digestive tract?
Solution
Epithelial Tissue
Bone is an example of what type of tissue?
Solution
Connective Tissue
Tissues
Fill in the blanks: ___________ connect muscle to bone, and ___________ connect bone to bone.
Solution
Tendons connect muscle to bone, and ligaments connect bone to bone.
Cell Outcomes
Choose the most correct answer. A cell that is capable of dividing in to many different types of tissue cells is called a:
Solution
Stem cells are considered pluripotent. While egg, or reproductive cells could divide into many different cells once fertilized, it is the stem cells that directly split into different types. Stem cells is the most correct answer choice.
Stem Cells
State two sources of stem cells in animals. [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood from newborns.
(Answers may vary...)
(Answers may vary...)
The Musculoskeletal System
Smooth muscle tissue contracts voluntarily
Solution
Smooth muscle tissue contracts involuntarily
Which of the following statements is not true?
Solution
Muscles cannot exert a 'push' force. Muscles only have tensile strength.
The musculoskeletal system does not include smooth muscle. Smooth muscles are part of involuntary muscle groups... like the digestive (GI tract), urinary (bladder), or circulatory systems (blood vessels).
Musculoskeletal muscle is voluntary (somatic), but smooth muscle involuntary (autonomic).
The musculoskeletal system does not include smooth muscle. Smooth muscles are part of involuntary muscle groups... like the digestive (GI tract), urinary (bladder), or circulatory systems (blood vessels).
Musculoskeletal muscle is voluntary (somatic), but smooth muscle involuntary (autonomic).
The Respiratory System
During exhalation the diaphragm relaxes and the rib cage contracts
Solution
True. (Animals have to respire actively with the diaphragm, whereas plants don't have to do anything, they passively respire through the stoma by the concentration gradient of gases).
Gas exchange between blood and the air occurs in the capillary sacs, across a cell wall by a process called diffusion.
Solution
alveoli
The Circulatory System
The smallest blood vessels are called
Solution
Capillaries
The function of the circulatory system is to
Solution
- Transport metabolic waste products away from the cells
- Transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body
- Exchange gases between the blood and the air
All of the above
- Transport metabolic waste products away from the cells
- Transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body
- Exchange gases between the blood and the air
Capillaries carry
Solution
Careful, capillaries carry both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, which undergoes gas exchange through diffusion. Carbon dioxide and other metabolic waste processes in deoxygenated blood are carried away in the blood stream.
The Circulatory System: Blood Components
Which of the following is the most plentiful component of blood?
Solution
Plasma is about 55% of blood volume, and red blood cells are 45%. Plasma contains plasma cells, electrolytes (ions such as Ca2+, Na+, HCO3-...), proteins, hormones, dissolved gases, and more.
Which of the following is primarily responsible for causing blot clots?
Solution
Platelets form a web-like matrix when activated, to clump and clot. This is good when sealing wounds, but bad when clumping occurs inside important blood vessels.
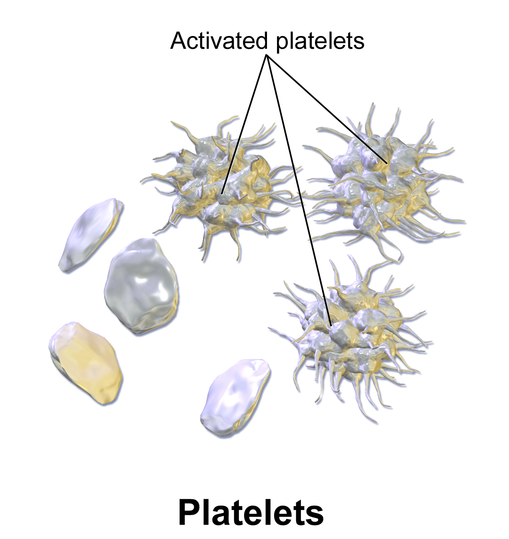
Creative Commons: BruceBlaus, 2013
 |
Red blood cells and platelets do not have a nucleus.
Solution
True, red blood cells and platelets do not have a nucleus. (White blood cells do have a nucleus).
The Circulatory System
The heart is made entirely of three different types of tissues.
Solution
Muscle, nerve, and connective tissue.
The Circulatory System
Arteries are defined as blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood.
Solution
Arteries are defined as blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. However, arteries do not always carry oxygenated blood. An example of arterial blood that is not oxygenated is the blood travelling from the heart to the lungs.
The Circulatory System
Deoxygenated blood coming from the body enters what part of the heart first? Solution
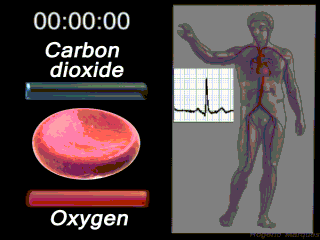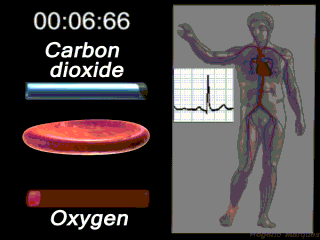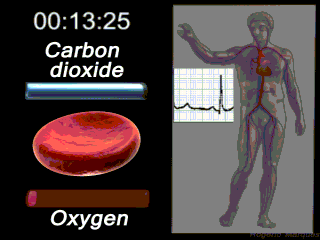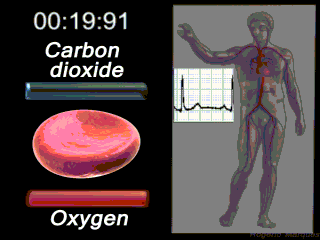 |
The Circulatory System
Describe at least two functions of the circulatory system. [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
- Transport gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the body.
- Transport nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and glucose.
- Transport metabolic wastes out of cells. Fight against infections.
- Transport gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the body.
- Transport nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and glucose.
- Transport metabolic wastes out of cells. Fight against infections.
The Digestive System: Components
Which of the following is not part of the digestive system?
Solution
Trachea is part of the respiratory system.
The liver and gall bladder are both accessory organs of the digestive system.
Solution
The accessory organs of the digestive system includes the: liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
The Digestive System: Functions
Water and nutrient absorption occurs mainly in the stomach.
Solution
While some absorption occurs in all different areas, water absorption occurs mainly in the large intestine. Nutrient absorption occurs mainly in the small intestine.
Bile is produced in the
Solution
Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder
The Nervous System
The brain is part of the peripheral nervous system
Solution
The brain is part of the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is the nerves that connect the rest of the body to the central nervous system.
The Nervous System
The smallest divisible cell component of the nervous system is the neuron.
Solution
The dendrites, nucleus, cell body, myelin, and axon come together to make up the neuron cell.
Cell Systems
The system that provides structural support for the body is the
Solution
Musculoskeletal system.
The nephron is part of which system?
Solution
Urinary system.
Cell Systems
Fill in the blanks regarding the interaction between the circulatory and respiratory systems, and the main organs of each system.
Solution
- The circulatory-respiratory interaction occurs at the ______(I)______-alveoli boundaries.
- The gas exchange occurs with ______(II)______ moving from the respiratory (alveoli) to the circulatory system (capillary), and carbon dioxide moving from the circulatory (capillary) to the respiratory system (alveoli).
- The gas exchange is driven by the concentration ______(III)______ of gases, always from high to low concentration.
- This movement of blood is driven by the ______(IV)______.
- The circulatory system collects many different metabolic waste products from the body, including carbon dioxide.
- The heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the ______(V)______, then pumps the oxygenated blood back to the heart to be distributed to the body again.
Hint
Clear
Info
I =
II =
III =
IV =
V =
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
- The circulatory-respiratory interaction occurs at the capillary-alveoli boundaries.
- The gas exchange occurs with oxygen moving from the respiratory (alveoli) to the circulatory system (capillary), and carbon dioxide moving from the circulatory (capillary) to the respiratory system (alveoli).
- The gas exchange is driven by the concentration gradient of gases, always from high to low concentration.
- This movement of blood is driven by the heart.
- The circulatory system collects many different metabolic waste products from the body, including carbon dioxide.
- The heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, then pumps the oxygenated blood back to the heart to be distributed to the body again.
II =
III =
IV =
V =
- The circulatory-respiratory interaction occurs at the capillary-alveoli boundaries.
- The gas exchange occurs with oxygen moving from the respiratory (alveoli) to the circulatory system (capillary), and carbon dioxide moving from the circulatory (capillary) to the respiratory system (alveoli).
- The gas exchange is driven by the concentration gradient of gases, always from high to low concentration.
- This movement of blood is driven by the heart.
- The circulatory system collects many different metabolic waste products from the body, including carbon dioxide.
- The heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, then pumps the oxygenated blood back to the heart to be distributed to the body again.
Plant Systems
Plant Systems: Photosynthesis
What molecule is missing from the equation below?
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Carbon dioxide, CO2.
(This is the carbon source for the glucose that is made in photosynthesis.)
(This is the carbon source for the glucose that is made in photosynthesis.)
Plant Systems: Carbon
Carbon is one of the major macronutrients in plants.
Where does a plant derive this macronutrient?
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Carbon dioxide, CO2, from the air.
(This is the carbon source for the glucose that is made in photosynthesis.)
Carbon is also a component of many other parts: cell wall, genetic material, proteins, etc...
(This is the carbon source for the glucose that is made in photosynthesis.)
Carbon is also a component of many other parts: cell wall, genetic material, proteins, etc...
Indoor plants are commonly used in offices or at home to remove CO2 and volatile organic compounds, and to increase O2. Of the options below, what property of plants would indicate the most effective plant for the highest rate of CO2 removal? Assume all other requirements of the plant are provided in excess.
Solution
While many of the answer choices appear correct, the plant with the fastest growth would use (sequester) carbon with the fastest rate. Since carbon is one of the major macronutrients in plants, it is required for use in many things, including growth. Fast growing plants is an indication of high CO2 use.
Plant Systems: Energy Production
The process in which plants convert light energy into chemical energy is called
Solution

Photosynthesis. (The light energy is transformed into, chemical energy stored as glucose)
Which of the following gases is a by-product of cellular respiration in plants?
Solution
A by-product is a secondary product made during the manufacture or synthesis of the main product. Energy is produced through cellular respiration and one of the main by-products is carbon dioxide, CO2.
Plant Systems: Energy Production
What molecule does a plant use to store its energy? Solution
 |
In plants, which of the following occurs both during the day and at night?
Solution
It is true that cellular respiration occurs both day and night. This process is necessary in both plants and animals to produce the energy required to sustain life.
Plant Systems: Energy Production and Storage
Carrots have taproot (root) systems while potatoes have tuber (stems) systems underground. Describe what is primarily stored in these systems, and explain the path it takes to get there.
Solution
Carrot taproots and potato tubers store starch, which comes from the glucose sugar produced in the chloroplasts in the leaf organs. This sugar is transported by the vascular tissue system from the leaf mesophyll (ground tissue system) down the phloem tissue.
The sugar produced by any plant is mainly stored in its root system.
Solution
Only some plants mainly store the sugar in the roots. It depends on the plant. Some plants store most of the sugar in the fruit, or in the flowers, or even in the stem...
Plant Cells and Systems
Copy the different classifications, for use up ahead... It's tricky to go without this.
 |
- Shoot system (flower, fruit, leaf, stem)
- Root system (only root)
- Leaf
- Stem
- Root
- Dermal
- Vascular
- Ground
- Epidermis
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Parenchyma
- ...
- Guard cells
- Stomata cells
- Stem cells
- ...
Plant Cells and Systems
Gas exchange occurs through the stomata in plant cells, which is part of the respiratory system in plants.
Solution
True. The stomata cells in plants are part of the dermal tissue system, on the outer layer of the plant, and are also considered part of the respiratory system. These are overlapping systems in the case of stomata...
The cells that regulate the opening and closing of the stomata pores in plants are called guard cells.
Solution
True. Stomata are pores in the surface of a leaf that allow gas exchange: oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapour. The cells that regulate the opening and closing of these pores are called guard cells.
Plant Systems
A plant with a very thick, waxy cuticle layer would most likely be found in what environment?
Solution
The cuticle is the outer layer of the plant tissue and is necessary to protect against infection and to prevent the plant from drying out. A thick, waxy cuticle would protect a plant from many things, including protection from water loss in hot, dry, or cold conditions, and to prevent the plant tissue from disintegrating in wet environments.

 |
Plant Systems
State the two main body (organ) systems of plants, and describe the main function of each system. [4]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The root system is responsible for absorbing nutrients and water for the plant, and for structural support. The shoot system is made of the rest of the plant (stem, leaves, and flowers) and is responsible for photosynthesis and reproduction.
What are the two main types of root systems that originate from meristem cells? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
1) Fibrous roots (like grass)
2) Taproots (like carrots, or radish, and trees) - can be primary, secondary, or tertiary
[Note: tubers like potatoes are not part of root system, its the stem, although there are some other tuberous roots. Note 2: adventitious roots are less common and do not originate from meristem.]
2) Taproots (like carrots, or radish, and trees) - can be primary, secondary, or tertiary
[Note: tubers like potatoes are not part of root system, its the stem, although there are some other tuberous roots. Note 2: adventitious roots are less common and do not originate from meristem.]
Plant Organs and Systems
Which of the following is not a part of the plant body system?
Solution
This is not one of the plant systems: "Chlorophyll tissue system". No such thing, it's false.
The 3 tissue systems in plants are:
- Dermal (outer layer)
- Vascular (fluid/nutrient transport)
- Ground (support and function)
The 3 tissue systems in plants are:
- Dermal (outer layer)
- Vascular (fluid/nutrient transport)
- Ground (support and function)
Plant Systems
The tissue system in plants responsible for distributing water and minerals throughout the plant is called the
Solution
Vascular tissue system consists of xylem and phloem.
Plant Systems: Division and Differentiation/Specialization
Cell division in plant cells occurs in the meristems.
Solution
True. Cell division in plant cells occurs in the meristems.
Name two of the regions of the plant where the stem cells are located. [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Stem cells are located with the meristem, is located in apical/terminal regions (at roots and shoots), and lateral (in vascular xylem/phloem tissue), and intercalary (along the stem, for width growth). [Also accept axial meristem, or adventitious meristem]
Apical meristem cells can differentiate into which of the following cell, tissue, or tissue systems?
Solution
Apical meristem cells differentiate into many different cell types to form many different tissues and tissue systems...
Apical meristem cells can become any of the 3 tissue systems:
↓
Dermal, Ground, Vascular
↓
Makes many different cell types and tissues
↓
...
↓
Dermal, Ground, Vascular
↓
Makes many different cell types and tissues
↓
...
Plant Tissue
Which of the following things are carried out within the parenchyma located within the mesophyll?
Solution
Parenchyma is a type of ground tissue within the mesophyll.
Mesophyll is the palisade/spongy layer in the middle layer of the leaf. Most of photosynthesis occurs here, as well as cellular respiration, and other metabolic processes, etc... Mesophyll cells contain a nucleus, so there are many nuclear processes occuring...
Plant Vascular Tissue System
Xylem tissue is only found in the stem organs of plants.
Solution
The xylem tissue is found in all three plant organs: roots, stems, and leaf. Its purpose is to distribute water and minerals from the roots to all other regions of the plant.
Which statement about xylem vascular tissue is incorrect?
Solution
- Xylem dies at maturity so it is hollow
- Xylem is located at the center of roots and stems
- Xylem is located within the mesophyll (in the middle layer of the leaf) near where the photosynthesis occurs, which requires lots of water
- Xylem can only transport water and minerals upward.
- Xylem dies at maturity so it is hollow
- Xylem is located at the center of roots and stems
- Xylem is located within the mesophyll (in the middle layer of the leaf) near where the photosynthesis occurs, which requires lots of water
- Xylem can only transport water and minerals upward.
Plant Tissue Systems
What part of the plant obtains water and what tissues transport this throughout the plant? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Roots absorb water and dissolved minerals, transported up the xylem (not phloem). When you water a plant, or give it fertilizers, it is absorbed at the root and being transported in the xylem system only.
What part of the plant obtains sugars and what tissues transport them throughout the plant? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Photosynthesis produces glucose in the mesophyll in the leaf, transported down the phloem (not xylem).
Plant Genetics
Within a plant, the genome is basically the same in every cell type.
Solution
True - the genome is the same. But what causes the differences in cell types in differentiation/specialization is the selective expression of genes. This results in different traits like size, color, etc...
Plant genes are proteins.
Solution
Plant genes are DNA, which encode for proteins. Genes are not proteins themselves. The selective expression creates different sets of proteins in different cell types.
Differences in plant cells only results from turing genes on or off.
Solution
It is not only on or off. Most of the time the gene expression is controlled as more or less, rather than on or off. Different parts of the same genome (DNA) are turned into proteins in different amounts. This difference creates different amounts of molecules like proteins in different cells, resulting in different cell types...
Plant Viruses
Describe one main example of a plant virus that is devastating to plants. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) was the first infectious virus to be discovered in plants in the 1900s. It reduces crop yield and desirability. [This one is most commonly used in classed, at school.]


Describe one main example of a plant virus that is purposefully cultivated by humans. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Tulip Breaking Virus (TBV) results in colorful variations in tulips, that are valuable to tulip buyers and create an economy in certain regions...
 [also accept: Tulip break virus, Lily streak virus, Tulip mosaic virus, Lily mosaic virus]
[also accept: Tulip break virus, Lily streak virus, Tulip mosaic virus, Lily mosaic virus]
 [also accept: Tulip break virus, Lily streak virus, Tulip mosaic virus, Lily mosaic virus]
[also accept: Tulip break virus, Lily streak virus, Tulip mosaic virus, Lily mosaic virus]
Plants and Genetic Engineering
Explain one positive example of genetic engineering in plants. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Genetically engineered crops are more resistant to weather and some pests, resulting in higher yields, and reducing the use of harmful pesticides.
[Also accept creation of larger fruits and vegetables, faster growth = greater yield...]
[Also accept the selective removal of allergens to make more palatable to more people]
(Answers may vary...)
[Also accept creation of larger fruits and vegetables, faster growth = greater yield...]
[Also accept the selective removal of allergens to make more palatable to more people]
(Answers may vary...)
Explain one negative example of genetic engineering in plants. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Genetic engineering is entering into uncharted territory where we may not fully understand the long-term health implications, or may be missing/overlooking some crucial problem.
[Also accept the problem with one company owning the patent and farmers owing royalties and buying from one source.]
[Also accept the genetic similarity of some genetically engineered plants means some pests can evolve, exploit, and devastate some crops with disease.]
(Answers may vary...)
[Also accept the problem with one company owning the patent and farmers owing royalties and buying from one source.]
[Also accept the genetic similarity of some genetically engineered plants means some pests can evolve, exploit, and devastate some crops with disease.]
(Answers may vary...)
Flashcards: Biology
| What is a unicellular organism? |
| An organism, such as an Amoeba or Paramecium, which is made of only 1 cell. |
| List from lowest order to highest order: Organ, Tissue, Organ system, Cell |
| Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system |
| What is one of the main differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? |
| Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus |
| What is the main difference between plant and animal cells? |
| Only plant cells have a cell wall (because this is the necessary structural component for plants) |
| What is an organelle? |
| Different structures/components within a cell |
| What cellular organelle is used for transport within the cell? |
| Cytoplasm |
| Which organelle is used for metabolism? |
| Mitochondria |
| Can cellular respiration occur in plants? |
| Yes |
| Do plant cells contain mitochondria? |
| Yes |
| Do animal cells contain chloroplasts? |
| No |
| What occurs during interphase? |
| The cell rests and can copy genetic material before mitosis (PMAT) starts |
| In which phase of cell division do the chromosomes first condense? |
| Prophase |
| What is the longest of the cellular phases? |
| Interphase |
| Is interphase part of mitosis? |
| No, interphase is before mitosis |
| In what phase of cell cycle do the chromatids split apart? |
| Telophase |
| How is cell division involved in cancer? |
| Cancer is linked with uncontrolled/unregulated cell division at an increased rate. |
| What is tissue? |
| A group of cells that perform a specialized, similar function |
| Which type of tissue is described as long, thin cells that conduct electrical impulses? |
| Nerve Tissue |
| The heart is an example of what type of tissue? |
| Muscle Tissue |
| Which tissue lines the digestive tract? |
| Epithelial Tissue |
| Bone is an example of what type of tissue? |
| Connective Tissue |
| What tissue connects bone to bone? |
| Ligaments |
| What is a stem cell? |
| A cell that is capable of dividing in to many different types of tissue cells |
| What are two sources of stem cells in humans? |
| Bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood from newborns |
| What type of muscle contracts involuntarily? |
| Smooth muscle |
| How do the diaphragm muscles control breathing? |
| The diaphragm contracts during inhalation and relaxes during exhalation |
| What are the sites of gas exchange in the lungs? |
| Alveoli |
| How are veins and arteries defined? |
| Veins carry blood to the heart, and arteries carry blood away from the heart |
| Do arteries always carry oxygenated blood? |
| No (for example the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs) |
| Describe two functions of the circulatory system |
| To transport metabolic waste products away from the cells and to transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. (Also acts to carry components of immune system) |
| What component of blood occupies the most volume? |
| Plasma |
| Where is bile produced? |
| In the liver |
| Plants respire through the stoma through what process? |
| Diffusion |
| What are the byproducts of cellular respiration in plants? |
| Carbon dioxide and water |
| What molecule does a plant use to store its energy? |
| Sugar (Glucose) |
Chemistry: Chemical Reactions & Naming
COMPOUNDS
Molecular/Covalent and Ionic
Match the properties, which are about covalent and ionic compounds.
Solution
Bonded with a transfer of electrons
Bonded with a sharing of electrons
Made of two or more non-metals
Made of a metal + a non-metal
Covalent
Ionic
Ionic = transfer of electrons between metal + a non-metal.
Molecular/covalent = sharing of electrons between two non-metals.
Molecular/covalent = sharing of electrons between two non-metals.
Forming Covalent Compounds
Which of the following elements is most likely to form a covalent, molecular compound?
Solution
Covalent, molecular compounds form between two non-metals. Sodium and calcium are metals. Carbonate is a charged, polyatomic ion. Neon is a noble gas and doesn't bond. Metals cannot make covalent compounds.
Identifying Covalent Compounds
Which of the following is a covalent compound?
Solution
Video
Covalent is two non-metals...
Binary Compounds
Al2O3 is an example of a binary compound.
Solution
A binary compound is made out of only two (different) elements. The subscript does not matter.
Identifying Compound Types: Molecular
Which of the following compounds is considered a molecular compound?
Solution
Molecular compounds consist of covalent bonds in which electrons are shared between 2 or more non-metals. Convalent compounds cannot contain ions (like SO42-, or CO32-).
Ions
Calcium (Ca) would tend to (hint: use the periodic table):
Solution
Video
Calcium is in group 2 on the periodic table. Group two elements have two valence electrons that are both lost when these elements form ions--turning into cations.
Ions
Chlorine would react and bond with each of the following except:
Solution
Chlorine and bromine are halogens, which tend to gain electrons to form negative anions. Ions that form the same charge do not bond. The ions in ionic bonds must be oppositely charged: a cation, then an anion.
Ionic Compounds
Which of the following ions would fit into this space indicated by 'Z' below?
Solution
Video
MgZ2
Magnesium is a metal, and will always form a cation (positively charged ion). This must react with an anion (negatively charged cation) in the right ratio.
Magnesium is a positive two charge, Mg2+ and the total negative charges must be the same amount, and opposite charge: -2... Since there must be two of these negative ions, it will be two -1 charges...
Magnesium is a positive two charge, Mg2+ and the total negative charges must be the same amount, and opposite charge: -2... Since there must be two of these negative ions, it will be two -1 charges...
Chemical Formulas
Complete the following table on paper, with the correct chemical formula for each compound.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Ag+ Cu2+ Fe3+ Ti4+
Cl-
O2-
PO43- ( ) ( )
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges using the criss-cross method. Look up the charges for the polyatomic ions. Remember to reduce the subscripts by the greatest common factor (if any).
Ag+ Cu2+ Fe3+ Ti4+
Cl- AgCl CuCl2 FeCl3 TiCl4
O2- Ag2O CuO Fe2O3 TiO2
PO43- Ag3PO4 Cu3(PO4)2 FePO4 Ti3(PO4)4
Use the criss-cross method to balance the charges with subscripts on the ions. Subscripts with a common factor reduce. For example...
Cu2O2 --> CuO
Or...
Ti2O4 --> TiO2
| Ag+ | Cu2+ | Fe3+ | Ti4+ | |
| Cl- | ||||
| O2- | ||||
| PO43- | ( ) | ( ) |
| Ag+ | Cu2+ | Fe3+ | Ti4+ | |
| Cl- | AgCl | CuCl2 | FeCl3 | TiCl4 |
| O2- | Ag2O | CuO | Fe2O3 | TiO2 |
| PO43- | Ag3PO4 | Cu3(PO4)2 | FePO4 | Ti3(PO4)4 |
Naming
When to Use All the Different Naming Systems
Compounds use different naming systems and it is important to know when to use each one.

Explain when the stock naming system is used, and how to use it. [3]
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Look at the flow chart, given above
The STOCK system is used for multivalent (more than one possible charge like Cu1+/Cu2+, or Au1+/Au3+) metals in ionic compounds (ionic is a metal + a nonmetal). The second word does not use roman numerals, only the first word does. (Sometimes, rarely, the classical system is used instead of stock IUPAC naming)
(Side-note: the diatomic gases HOFBrINCl do not use any naming system, just name the element)
(Side-note: the diatomic gases HOFBrINCl do not use any naming system, just name the element)
Explain when the prefix naming system is used, and how to use it. [3]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Look at the flow chart, given above
The PREFIX system is used for covalent compounds (covalent is two non-metals), not ionic compounds. A prefix is only used on the first word if 2 or more, and a prefix is always used on the last word. The second word ends with -ide. (Note that mono is only used in the second part of the name, never in the first part. CO2 is not monocarbon dioxide...)
Explain when the general naming system is used, and how to use it. [3]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Look at the flow chart, given above
The GENERAL system is used if the ionic compound is not multivalent. Just name the first word like it appears on the periodic table and the second word ends with -ide (for example: Na20 is sodium oxide).
Naming Molecular/Covalent
Prefix Naming
Order the prefixes, with lowest at the top, by dragging them around.
Solution
deca
tri
penta
di
hepta
octa
tetra
hexa
nona
mono
You need to know this list for naming all the covalent compounds, coming up next...
1) mono
2) di
3) tri
4) tetra
5) penta
6) hexa
7) hepta
8) octa
9) nona
10) deca
1) mono
2) di
3) tri
4) tetra
5) penta
6) hexa
7) hepta
8) octa
9) nona
10) deca
Naming Covalent Molecules
Name the molecule. (Hint: use the prefix naming system)
Solution
H2O
The prefix naming system is used in covalent compounds (between two non-metals). The prefix comes from the subscript number indicating number of each atom in the molecule.
_________ + _________
Tee first word uses a prefix if 2+ atoms...
The second word uses a prefix if 1+ atoms (always)...
The second word uses a prefix if 1+ atoms (always)...
Practice Naming Compounds: Molecular/Covalent
Name the following compounds, using the prefix system.
CO
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
carbon monoxide
(not monocarbon monoxide - because mono never goes on the 1st word.)
(not monocarbon monoxide - because mono never goes on the 1st word.)
NO
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
nitrogen monoxide
(Remember to only use mono on the second word, never the first).
(Remember to only use mono on the second word, never the first).
N2O
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
dinitrogen monoxide
(drop the 'o' on the mono suffix)
(drop the 'o' on the mono suffix)
B2H6
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
diboron hexahydride
(Still add the suffix -ide to the end of hydrogen = hydride)
(Still add the suffix -ide to the end of hydrogen = hydride)
CH4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
carbon tetrahydride
PCl5
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
phosphorus pentachloride
CO2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
carbon dioxide
N2F4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
dinitrogen tetrafluoride
P2O5
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Determine the number of each element, and don't forget to add the suffix.
diphosphorus pentoxide
(drop the 'a' on the penta suffix)
(drop the 'a' on the penta suffix)
Practice Writing Formulas: Molecular/Covalent
Write the chemical formula for the following compounds.
Dihydrogen monosulfide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
H2S
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Nitrogen trihydride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
NH3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Diphosphorus trisulfide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
P2S3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Silicon tetrachloride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
SiCl4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Nitrogen triiodide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
NI3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Dinitrogen trioxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
N2O3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Sulfur trioxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
SO3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Trioxygen
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
The prefix in-front of each element indicates the amount.
O3
(common name: ozone)
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
(common name: ozone)
Correcting Common Mistakes
Find what's wrong with the following names or formulas, and correct them.
Mononitrogen monoxide
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Where should prefixes be used?
Covalent compounds using the prefix naming system never have mono in the first name.
The correct name for NO:
nitrogen monoxide
(This is like carbon monoxide, which you may know is CO).
The correct name for NO: nitrogen monoxide (This is like carbon monoxide, which you may know is CO).
Dihydrogen sulfide
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Where should prefixes be used?
The last name always has a prefix, even if it's just one.
The correct name for H2S:
dihydrogen monosulfide
The correct name for H2S: dihydrogen monosulfide
C1F4
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
What subscripts should not be used?
Don't write subscripts of 1.
The correct formula is just:
CF4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
The correct formula is just: CF4
Naming Ionic
Practice Naming Compounds: Ionic
Name the following ionic compounds. Remember that ionic compounds consist of a metal plus a non-metal.
MgO
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Mg2+O2-
Magnesium is not multivalent, so no roman numerals are required. Don't use prefix naming with ionic compounds (metal plus non-metal).
magnesium oxide
Magnesium is not multivalent, so no roman numerals are required. Don't use prefix naming with ionic compounds (metal plus non-metal). magnesium oxide
AlCl3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Al3+Cl1-
Aluminum is not multivalent, so no roman numerals are required.
aluminum chloride
Aluminum is not multivalent, so no roman numerals are required. aluminum chloride
InF3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
indium fluoride
Na2O
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
sodium oxide
CaSe
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
calcium selenide
BaI2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
barium iodide
ScF3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
scandium fluoride
ZrBr4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
zirconium bromide
Practice Writing Formulas: IONIC
Write the chemical formula for the following compounds.
Sodium sulfide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
 |
Calcium sulfide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
Using criss-cross with the ions... Ca2+ S2-
The 2s cancel, so there's one of each...
CaS
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
The 2s cancel, so there's one of each...
CaS
Silver fluoride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
Using criss-cross with the ions... Ag1+ F1-
AgF
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
AgF
Zinc bromide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
Using criss-cross with the ions... Zn2+ Br1-
ZnBr2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
ZnBr2
Gallium oxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
Ga2O3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Lithium iodide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
LiI
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Germanium oxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges
GeO2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Zirconium nitride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges. Use the most common ion charge.
Zr4+ + N3-...
Zr3N4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Zr3N4
Aluminum chloride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Start with the charges on the ions, and then use the criss-cross method to balance the charges. Use the most common ion charge.
AlCl3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Correcting Common Mistakes
Find what's wrong with the following names or formulas and correct them.
disodium monoxide
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Ionic compounds don't use the prefix naming system. The correct name would be:
sodium oxide
The roman numeral in, copper(II) sulfate/sulphate, indicates that there are two atoms of copper per molecule.
Solution
The roman numeral indicates the charge (or oxidation number) of the multivalent cation.
scandium(III) phosphide
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Don't use the stock roman numeral numbering system for monovalent elements - elements that only have one valence or possible charge.
Scandium can only ever have a 33+ charge and is implied in its name.
Correct name:
scandium phosphide
Correct name: scandium phosphide
Naming Polyatomics
Polyatomic Ions, Quantitative Intro
How many atoms of Oxygen are in 2 molecules of aluminum nitrate?
Solution
Al(NO3)3
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
atoms
Hint Unavailable
The subscript, 3 multiplies to the 3 oxygens so 1 molecule of aluminum nitrate has 9 oxygens.
2 molecules of aluminum nitrate have 18 oxygens.
2 molecules of aluminum nitrate have 18 oxygens.
Polyatomic Anions
The oxides of chlorine and bromine form four different polyatomic anions with different numbers of oxygen atoms, x. Rank the naming system in the order of decreasing number of oxygens from top to bottom.
Solution
ClOx- BrOx-
_________-ite
per-_________-ate
hypo-_________-ite
_________-ate
In terms of the number of oxygens:
"Per-" is highest
"Hypo-" is lowest
"-ate" is higher
"-ite" is lower
ClO4–
perchlorate
ClO3–
chlorate
ClO2–
chlorite
ClO–
hypochlorite
BrO4–
perbromate
BrO3–
bromate
BrO2–
bromite
BrO–
hypobromite
"Per-" is highest
"Hypo-" is lowest
"-ate" is higher
"-ite" is lower
| ClO4– | perchlorate
|
| ClO3– | chlorate
|
| ClO2– | chlorite
|
| ClO– | hypochlorite
|
| BrO4– | perbromate
|
| BrO3– | bromate
|
| BrO2– | bromite
|
| BrO– | hypobromite
|
Which of the following polyatomic anions is sulfate/sulphate?
Solution
An anion has a negative charge
Sulphate/Sulfate is SO42-
(Sulphite/Sulfite is SO32-)
The suffix (ending) with '-ate' has more oxygens because it ate more...
Sulphate/Sulfate is SO42-
(Sulphite/Sulfite is SO32-)
The suffix (ending) with '-ate' has more oxygens because it ate more...
Making Ionic Compounds from Ions using the Criss-Cross Method (Including Polyatomic)
Compose the following ions into their salt/ionic compound by balancing the charges, and then name the compound. Put the formula of the compound in the box provided below, using proper capitalization and subscripts. [2]
Ca2+, PO43-
Solution
Video
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
NH4+, CO32-
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Practice Naming Compounds: POLYATOMICS
Name the following compounds containing polyatomic ions.
Ca(NO3)2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
calcium nitrate
(Note it's not calcium dinitrate because we don't use the prefix naming system on polyatomic ions).
(Note it's not calcium dinitrate because we don't use the prefix naming system on polyatomic ions).
Al2(SO3)3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
aluminum sulfite
(Don't use prefix naming system: aluminum trisulfite)
(Don't use prefix naming system: aluminum trisulfite)
(NH4)SO4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
ammonium sulfate
This is an ionic compound with polyatomic ions.
This is an ionic compound with polyatomic ions.
AgCN
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
silver cyanide
Zn(CH3COO)2, a.k.a. Zn(C2H3O2)2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
zinc acetate
Al(HCO3)3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
aluminum bicarbonate
Be3(PO3)2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
beryllium phosphite
Zn(ClO2)
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
zinc chlorite
Mg(OH)2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
magnesium hydroxide
KMnO4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
potassium permanganate
Practice Writing Formulas: POLYATOMICS
Write the chemical formula for the following compounds with polyatomic ions.
Sodium bicarbonate
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Na+ + HCO3-
NaHCO3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
NaHCO3
Magnesium perchlorate
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Mg2+ + ClO4-
Mg(ClO4)2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Mg(ClO4)2
Diammonium sulfide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Diammonium is two (di) ammonium ions.
NH4+ + S2-
(NH4)2S
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
NH4+ + S2-
(NH4)2S
Tin(II) sulfite
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sn2+ + SO32-
SnSO3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
SnSO3
Strontium cyanide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sr(CN)2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Silver phosphite
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Ag3PO3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Potassium hydroxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
KOH
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Aluminum acetate (C2H3O2)
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Al(C2H3O2)3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Correcting Common Mistakes
Find what's wrong with the following names or formulas and correct them.
nitrogen-tetrahydride bromide
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Don't try to name polyatomic ions as molecular/covalent compounds. Use the name of the polyatomic ion. NH4Br is just ammonium bromide.
Sulfite: SO3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
This may be a bit tricky because SO3 is not polyatomic when it's by itself. You can tell because it is not bound to a metal cation in-front, like __SO3.
SO3 is a covalent compound by itself - so you name it with the prefix system.
= sulfur trioxide
SO3 is a covalent compound by itself - so you name it with the prefix system.
= sulfur trioxide
Sodium Sulfur Oxide: Na2SO3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Na2SO3 is an ionic compound with a monovalent metal (and a polyatomic anion), so it is named using the general naming system.
= sodium sulfite.
= sodium sulfite.
Naming Multivalent
Naming Molecules: Ionic → Multivalent
Name the molecule using the stock naming system: Ni2O3
Solution
Video
Multivalent metals (metals that could have different charges like Ni2+ or Ni3+) need to have the charge represented by roman numerals without a space between the cation and roman numeral.
The oxygen anion oxygen begins with a prefix representing the number of atoms, and it ends with the suffix -ide indicating that it is an ion.
Stock: Nickel(III) Oxide
(Classical system: Nicklic Oxide)
The oxygen anion oxygen begins with a prefix representing the number of atoms, and it ends with the suffix -ide indicating that it is an ion.
Stock: Nickel(III) Oxide
(Classical system: Nicklic Oxide)
Practice Naming Compounds: Multivalent
Name the following compounds using the stock system.
CuS
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Cu2+S2-
Copper is multivalent (Cu1+, Cu2+) so roman numerals are required.
copper(II) sulfide
Copper is multivalent (Cu1+, Cu2+) so roman numerals are required.
copper(II) sulfide
CuCl2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
copper(II) chloride
FeI3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Iron is multivalent (Fe2+, Fe3+) so use the stock naming system:
iron(III) iodide
iron(III) iodide
SnH4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sn4+ + H-1
tin(IV) hydride
tin(IV) hydride
CoPO4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Co3+ + PO43-
cobalt(III) phosphate
cobalt(III) phosphate
AuP
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Au3+ + P3-
gold(III) phosphide
gold(III) phosphide
TiS2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Ti4+ + S2-
titanium(IV) sulfide
titanium(IV) sulfide
Hg2O
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Hg1- + O2-
mercury(I) oxide
mercury(I) oxide
Practice Writing Formulas: MULTIVALENT
Write the chemical formula for the following compounds with multivalent ions.
mercury(II) fluoride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
HgF2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
copper(I) oxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Using criss-cross with the ions... Cu1+ O2-
Cu2O
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Cu2O
copper(I) sulfide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Using criss-cross with the ions... Cu1+ S2-
Cu2S
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Cu2S
manganese(II) nitride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Mn2+ + N3-
Mn3N2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Mn3N2
platinum(II) oxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Pt2+ + O2-
PtO
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
PtO
nickel(III) oxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Ni3+ + O2-
Ni2O3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Ni2O3
lead(IV) chloride
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Pb4+ + Cl-
PbCl4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
PbCl4
antimony(V) phosphide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sb5+ + P3-
Sb3P5
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Sb3P5
chromium(VI) oxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Cr6+ + O2-
Cr2O6
= CrO3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
= CrO3
Correcting Common Mistakes
Find what's wrong with the following names or formulas and correct them.
iron(III) triiodide
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The stock naming system is used without using prefixes. The correct name:
iron(III) iodide
We know there must be 3 Iodide atoms for each Fe3+ because the charge on each iodide is only I1-.
Sn2O2
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sn2+ + O2-
Using the criss-cross method, the subscripts will reduce to the lowest form:
= SnO
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Using the criss-cross method, the subscripts will reduce to the lowest form:
= SnO
Naming Multivalent and Polyatomic
Practice Naming Compounds: Multivalent & Polyatomic
Name the following compounds using the systematic stock naming system.
Cu2+, SO42-
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
CuSO4
copper(II) sulphate, [aka copper(II) sulfate]
copper(II) sulphate, [aka copper(II) sulfate]
HgHCO3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Hg+1 + HCO3-
mercury(I) bicarbonate
mercury(I) bicarbonate
Fe3(PO3)2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Fe2+ + PO33-
iron(II) phosphite
iron(II) phosphite
Sn(CH3COO)4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sn4+ + CH3COO1-
tin(IV) acetate
tin(IV) acetate
Au2SO4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Au+1 + SO42-
gold(I) sulphate, [aka gold(I) sulfate]
gold(I) sulphate, [aka gold(I) sulfate]
Co(ClO2)3
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Co3+ + ClO2-
cobalt(III) chlorite
cobalt(III) chlorite
Pd(MnO4)4
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Pd4+ + MnO4-1
palladium(IV) permanganate
palladium(IV) permanganate
Mn(NO3)2
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Mn2+ + NO3-1
manganese(II) nitrate
manganese(II) nitrate
Practice Writing Formulas: Multivalent & Polyatomic
Write the chemical formula for the following compounds.
tin(II) bicarbonate
Solution
Tin (Sn) has a 2+ charge, bicarbonate (HCO3) has a 1- charge.
Use the criss-cross method to determine the subscripts on each ion.
Sn2+(HCO31-)
= Sn1(HCO3-)2
= Sn(HCO3-)2
Use the criss-cross method to determine the subscripts on each ion.
Sn2+(HCO31-)
= Sn1(HCO3-)2
= Sn(HCO3-)2
platinum(IV) nitrite
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses.
Pt4+ + NO2-1
Pt(NO2)4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Pt(NO2)4
iron(III) cyanide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses.
Fe3+ + CN-
Fe(CN)3
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Fe(CN)3
gold(I) acetate (C2H3O2-)
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses.
Au+1 + C2H3O2- or CH3COO-
AuC2H3O2
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
AuC2H3O2
tungsten(V) hydroxide
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses.
W5+ + OH-
W(OH)5
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
W(OH)5
vanadium(IV) bicarbonate
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses.
V4+ + HCO3-1
V(HCO3)4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
V(HCO3)4
manganese(VI) carbonate
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses. Make sure to reduce the subscripts by the greatest common factor.
Mn6+ + CO32-
Mn2(CO3)6
Mn(CO3)3
(After criss-cross, reduce fully from 2:6 to 1:3)
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Mn(CO3)3
(After criss-cross, reduce fully from 2:6 to 1:3)
tin(IV) phosphate
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Balance the charges of the ions. Look up the polyatomic ions. Multivalent ions show their charge in parentheses.
Sn4+ + PO33-
Sn3(PO4)4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Sn3(PO4)4
Correcting Common Mistakes
Find what's wrong with the following names or formulas and correct them.
SnNO3 [with tin(IV)]
Solution
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Tin Sn4+, & nitrate, NO3-1...
Makes Sn(NO3)4
⁰
¹
²
³
⁴
⁵
⁶
⁷
⁸
⁹
⁻
⁺
⁽
⁾
₀
₁
₂
₃
₄
₅
₆
₇
₈
₉
₋
₊
₍
₎
Makes Sn(NO3)4
Sodium(II) bromide
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Sodium is not multivalent so it does not use the stock roman numeral naming system. It can only be Na+1.
The name is just sodium bromide.
The name is just sodium bromide.
EQUATIONS & REACTIONS
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balance the following equations. Balance the metal, or carbon, or first non-metal first. Then balance the hydrogens (if any). Last, balance the diatomic molecule like O2.
N2 + O2 N2O5
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
N2 + O2 N2O5
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Generally: balance metals first (if any), balance polyatomic ions as whole units, and balance diatomic molecules last.
C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Generally: balance metals first (if any), balance polyatomic ions as whole units, and balance diatomic molecules last.
C6H14 + O2 CO2 + H2O
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
C6H14 + O2 CO2 + H2O
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Generally: balance metals first (if any), balance polyatomic ions as whole units, and balance diatomic molecules last.
Al(OH)3 + H2CO3 Al2(CO3)3 + H2O
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Al(OH)3 + H2CO3 Al2(CO3)3 + H2O
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Generally: balance metals first (if any), balance polyatomic ions as whole units, and balance diatomic molecules last.
Writing Word Equations for Simple Chemical Reactions
The word equation for the following reaction shown below is: hydrogen + oxygen ↔ water.
Solution
Know the formulas of the basic compounds, hydrogen, oxygen, and water. It is common and not considered incorrect, for the word equation to include 'water' instead of 'dihydrogen monoxide'.
Writing Chemical Reactions from Word Equations
Write the chemical reaction for the following pseudo-word equations. Make sure to balance the equation and include the physical states.
The reaction of solid copper(II) oxide with hydrogen gas to form solid copper metal and water.
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
CuO(s) + H2 (g) Cu(s) + H2O(l)
The incomplete combustion of butane (C4H10) gas to form carbon monoxide gas and water vapor.
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
2C4H10 (g) + 9O2 (g) 8CO(g) + 10H2O(g)
The reaction of aqueous ammonia with aqueous hydrochloric acid to form aqueous ammonium chloride.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
NH3 (l) + HCl(aq) NH4Cl(aq)
Solid potassium metal reacts vigorously with liquid water to form hydrogen gas and aqueous lithium hydroxide.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + H2 (g)
When heated, solid calcium carbonate decomposes into solid calcium oxide and carbon dioxide gas.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
→+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
CaCO3 (s) CaO(s) + CO2 (g)
Highly exothermic reaction between solid aluminum and iron(III) oxide forms solid iron and aluminum oxide.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) 2Fe(s) + Al2O3 (s)
Chemical and Physical Changes
Explain why dissolving sodium chloride into water is a chemical change, while dissolving glucose (sugar) into water is a physical change. [4]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Think about the types of intramolecular bonds and how this is related to dissolving. Think about the definition of a chemical change, versus the definition of a physical change.
Sodium chloride NaCl(s) is a salt, and the ionic bonds between the 'Na' cation and 'Cl' anion are broken apart when they dissociate in the solution. Chemical changes change the bonding of the molecules, while physical changes do not change the bonding.
See the difference between the two reaction equations... Only one breaks apart.
The sugar molecule C6H12O6 (s) has covalent bonds so does not break apart when it is dissolved (solvated) into water. Physical changes only change the phase state of a compound without rearranging/changing any bonding, e.g. just solid to aqueous, or gas to a liquid.
The sugar molecule C6H12O6 (s) has covalent bonds so does not break apart when it is dissolved (solvated) into water. Physical changes only change the phase state of a compound without rearranging/changing any bonding, e.g. just solid to aqueous, or gas to a liquid.
Chemical and Physical Changes
Which two of the following causes a chemical change when dissolved in water?
Solution
Chemical changes are a change in the chemical bonding in a substance.
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, they separate into their aqueous (aq) ions (positive cation, and negative anion) and this is considered a chemical change.
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, they separate into their aqueous (aq) ions (positive cation, and negative anion) and this is considered a chemical change.
Evidence of Chemical Reaction Occurrence
A student is mixing some chemicals in a safe, controlled laboratory. Two liquids are mixed without heating or cooling. Which of the following is not evidence that a chemical reaction has occurred or is occurring?
Solution
Evaporation is a physical phase change from a liquid to a gas, therefore it is not a chemical reaction...
Other evidence a chemical reaction has occurred: change in temperature, production of light, or even odor...
[If the substance evaporated, and left behind an ionic compound, then this would be a chemical change when the dissolved ions reform an ionic bond.]
Other evidence a chemical reaction has occurred: change in temperature, production of light, or even odor...
[If the substance evaporated, and left behind an ionic compound, then this would be a chemical change when the dissolved ions reform an ionic bond.]
Density and Mass of Matter
Heating 1.0L of liquid water in a closed container will make it lighter when it converts to a gas.
Solution
While heating the water may change the phase from liquid to a solid, in a closed container the amount of matter is constant so there will be a constant mass.
Increasing the kinetic molecular energy of the water atoms will not decrease their mass.
Increasing the kinetic molecular energy of the water atoms will not decrease their mass.
The Law of Conservation of Mass
For the following reaction with 100.0 g of H2(g), approximately how much of the product will form if the reaction is performed in a closed environment?
Solution
Video
Total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products. Mass is 100% conserved in an isolated (insulated and closed) system, and in a closed system the mass is conserved by close to 100%.
The Law of Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that for any closed system (to transfers of matter and energy) the mass of the system is conserved.
Given the oxidation reaction of copper (II) below, if the sample increased in mass by over 150% during the course of the reaction, explain the cause of this change in mass. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Think about what goes into a reaction, and where the mass might come from.
The increase in mass is due to the oxygen gas from the air, bonding to the copper.
For example with an initial amount 10.0g of solid copper, the final mass of CuO would be 25.04 g !
For example with an initial amount 10.0g of solid copper, the final mass of CuO would be 25.04 g !
10.0g of Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) reacts in the following reaction in a container with no lid. If 5.3g of products are leftover, what explains the mass going from 10.0g to 5.3g?
Solution
Video
10.0g of reactant is still forming 10.0g of product, it's just that some of the product is a gas that doesn't get included when the products are weighed on the scale in the lab.
Simple Solubility Guidelines
In water, an ionic compound containing sodium (Na+) and carbonate (CO32-) will be
Solution
The 7 Chemical Reactions
Which of the following is not one of the seven general types of chemical reactions?
Solution
There are 7 general types of chemical reactions. Most people are only responsible for the first 4 or 5 main reaction types in this list.
- Synthesis: A + B --> AB
- Decomposition: AB --> A + B
- Single Displacement: A + BC --> B + AC
- Double Displacement: AB + CD --> AD + CB
- Combustion: carbon compound + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
- Neutralization (acid, base reactions)
- Corrosion (like, rusting)
A chemical reaction occurs when bonds are broken or new bonds are formed.
Vaporization is not a chemical reaction because the atom or molecule does not change bonding in any way if it's just a phase change.
- Synthesis: A + B --> AB
- Decomposition: AB --> A + B
- Single Displacement: A + BC --> B + AC
- Double Displacement: AB + CD --> AD + CB
- Combustion: carbon compound + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
- Neutralization (acid, base reactions)
- Corrosion (like, rusting)
Vaporization is not a chemical reaction because the atom or molecule does not change bonding in any way if it's just a phase change.
Match the reaction types with the examples.
Solution
Synthesis
Decomposition
Single Displacement
Double Displacement
2H2O → 2H2 + O2
Ca + 2NaBr → 2Na + CaBr2
Na2CO3 + CuSO4 → Na2SO4 + CuCO3
N2 + 2O2 → 2NO2
Match with the general equations for each...
- Synthesis: A + B --> AB
- Decomposition: AB --> A + B
- Single Displacement: A + BC --> B + AC
- Double Displacement: AB + CD --> AD + CB
- Synthesis: A + B --> AB
- Decomposition: AB --> A + B
- Single Displacement: A + BC --> B + AC
- Double Displacement: AB + CD --> AD + CB
Synthesis Reactions I
Complete the synthesis reactions, then balance. (Practice naming the products in your own notes).
H2 + O2 ______________
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
H2 + O2
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
2H2 + O2 2H2O
Ca + O2 ______________
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Ca + O2
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
2Ca + O2 2CaO
N2 + H2 ______________
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
N2 + H2
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
N2 + 3H2 2NH3
Synthesis Reactions II
Complete the synthesis reactions, then balance and name the products. A metal or metallic oxide will react with oxygen or carbon dioxide to form an ionic compound. A non-metallic oxide will react with water to form its resulting acid.
Fe + O2 ______________
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Fe + O2
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
A metal or metallic oxide will react with oxygen or carbon dioxide to form an ionic compound.
N2O5 + H2O ______________
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
N2O5 + H2O
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
A non-metallic oxide will react with water to form its resulting acid.
P2O5 + H2O ______________
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
P2O5 + H2O
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
A non-metallic oxide will react with water to form its resulting acid.
Simple Chemical Reactions
Scientists don't know how to effectively turn carbon dioxide into solid, elemental carbon plus oxygen yet, but if they did what would the most abundant other product be?
Solution
Video
Oxygen forms a diatomic gas, O2. This is a decomposition reaction.
Predicting Chemical Reactions
Which of the following reactions is a single displacement reaction?
Solution
Generally, the first atom in the ionic compound (B) gets replaced by the lone atom (A)...
A + BC → B + AC
Single Displacement Reactions: A + BC → B + AC
Complete the following single displacement reactions.
Metal Replaces other Metal, in Metal + Ionic Compound:
Solution
Video
Al(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) gas + salt
Hint
Clear
Info
+ ( ) →+ ( )
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
Metal Replaces Hydrogen, in Metal + Acid:
Solution
Mg(s) + HCl(aq) gas + salt
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
Halogens Replace Halogens:
Solution
F2(g) + NaCl(aq) gas + salt
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
Double Displacement Reactions: AB + CD → AD + CB
What's wrong with the double displacement reaction below? Correct the mistake.
Solution
AB + CD → AD + BC
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
The cation (C) should go first, and the anion (B) should go last in the product as: CB
Corrected:
AB + CD → AD + CB
Corrected: AB + CD → AD + CB
Double Displacement Reactions: AB + CD → AD + CB
The reaction between sodium carbonate and copper (II) sulfate/sulphate proceeds as follows. Determine the identity of compound 'Z' below.
Solution
This is a double displacement reaction, where the metals exchange positions...
Double Displacement Reactions: AB + CD → AD + CB
Complete the following double displacement reaction.
Metals Replace Metals
AgNO3(aq) + KI(aq) aqueous compound + solid compound
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
NaClO3 (aq) + MgF(aq) ______________
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
+ →+ ( )
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Write the compounds first, then balance. Make sure to include physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
2NaClO3(aq) + MgF2(aq) 2NaF(aq) + Mg(ClO3)2(aq)
Acids and Bases
Acidity and alkalinity depends on the concentration of hydronium and hydroxide ions relative to one another in the same solution. A solution is considered basic under which condition?
Solution
The solution is basic (alkaline) when the concentration of hydroxide ions, [OH-] is greater than the proton or hydronium ions. This is because in the same container with the same volume, the total number of moles of the alkaline hydroxide makes the solution alkaline overall.
Acid Base Neutralization
Hydrochloric acid neutralizes sodium hydroxide base in the following reaction. What are the products of this reaction?
Solution
Acid + Base ↔ Salt + Water...
Characteristics of Acids and Bases
Litmus is a water-soluble dye extracted from several different species of lichen plants, such as Roccella tinctoria or Dendrographa leucophoea. An unknown solution of clear liquid is tested to see if it is acidic or alkaline/basic by dipping red and blue litmus paper in. The red litmus paper does not change colour, however the blue litmus paper changes to a pinkish-red colour. Which of the following characteristics would this solution have?
Solution
Acids: sour, corrosive to metals, turns blue litmus red.
Bases: bitter, feel slippery, caustic to living tissues, turns red litmus blue.
Bases: bitter, feel slippery, caustic to living tissues, turns red litmus blue.
The pH Scale
Order the following chemicals from low to high pH (from top to bottom).
Solution
Stomach acid (HCl)
Household bleach
Baking soda
Distilled Water
Vinegar
Rainwater
Remember that acids have low pH and bases have higher pH...
Stomach acid (HCl), Vinegar, Rainwater, Distilled Water, Baking soda, Household bleach.
Stomach acid (HCl), Vinegar, Rainwater, Distilled Water, Baking soda, Household bleach.
Identifying Acids and Bases
Which of the following mixtures would result in a neutralization reaction? Solution
| Mixture | Compound 1 | Compound 2 |
| A | HCl | HNO3 |
| B | K2SO4 | H2O |
| C | OH- | H2CO3 |
| D | CH3COO- | NaOH |
Acid = H2CO3
Base = OH-
Naming Acids and Bases
What is the chemical formula for the following common compound?
Solution
Phosphoric acid
This is a common, weak acid: H3PO4
Common Household Acids and Bases
The following table contains the most common household chemicals that you need to know for school this year. The table has only one error in it, what is the common name of the chemical that has an error in its description. Solution
| Common Name | Chemical Name | Formula | Acid or a Base |
| Vinegar | Acetic Acid | CH3COOH | Acid |
| Baking Soda | Sodium Bicarbonate | NaHCO3 | Base |
| Ammonia Cleaner | Ammonia | NH3 | Base |
| Lye Oven Cleaner | Sodium Hydroxide | NaOH | Acid |
| Bleach | Sodium Hypochlorite | NaClO | Base |
Acid Base Applications
The following substances have been deemed non-toxic by a safety regulator and are approved for consumption. A chemist is trying to decide which to use for manufacturing a brand of pills to relieve inflamed stomach acids, sometimes known as 'heartburn'. Which of the following would be the best choice for this? Solution
| Substance | pH Range |
| LMN | 4.5 - 4.8 |
| PQR | 6.5 - 6.6 |
| FGH | 7.2 - 7.8 |
| JKL | 8.7 - 9.4 |
| XYZ | 10.7 - 11.5 |
Flashcards: Chemistry
| Alkali earth metals are located in what group? |
| Group 1 |
| Calcium (Ca) is located in group 2 so it would tend to ________ 2 electrons |
| Lose |
| Explain why chlorine and bromine would not react to form a compound |
| Both of these elements tend to gain electrons and become negatively charged. These similar charges would repel. |
| What is the Sulfide ion? |
| S2- |
| What is the chemical formula of the carbonate ion? |
| CO32- |
| What type of reaction is this? A + B → AB |
| Synthesis |
| What type of reaction is this? AB → A + B |
| Decomposition |
| What type of reaction is this? A + BC → B + AC |
| Single displacement |
| What type of reaction is this? AB + CD → AD + CB |
| Double displacement |
| What type of reaction is this? H(A) + (B)OH → AB + H2O |
| Neutralization |
| What type of reaction is this? CxHy + O2 → CO2 + H2O |
| Combustion |
| What is the chemical formula of the ammonium polyatomic ion? |
| NH4+ |
| When an ionic compound dissociates by dissolving in water, is this considered a physical or chemical change? |
| This is a chemical change because the chemical bonding of the molecule is changing. |
| An analysis of the contents of a solution shows the following: [H3O+] > [OH-] Is this acidic or basic? |
| Acidic |
| What are the products of a neutralization reaction between an acid and a base? |
| A salt and water |
| What is the common name of this acid? H2SO4 |
| Sulfuric acid |
| What is the common name of this acid? HNO3 |
| Nitric acid |
| What is the common name of this acid? H3PO4 |
| Phosphoric acid |
| What is the common name of this acid? H2CO3 |
| Carbonic acid |
| What is the common name of this acid? HCl |
| Hydrochloric acid |
Earth & Space Science: Climate Change
Terminology
In the following statement, what does anthropogenic mean? Some anthropogenic greenhouse gases can cause acid rain.
Solution
Caused by humans... for example, burning of fossil fuels resulting in various things like acid rain, rise in greenhouse gases...
Convection
Convection is the movement of heat in a fluid (i.e. a liquid or a gas).
Solution
True. For example, the movement of air in the atmosphere as wind. Or the movement of currents in the oceans...
Energy Transfer
Name the main processes by which energy can be transferred in the following situations Solution
| Space | Atmosphere | Water | Ground | |
| Energy Transfer(s): | I | II | III | IV |
Convection can occur in the air of the atmosphere or the water of oceans/lakes/rivers, but not in the vacuum of space because it depends on the presence of particles/molecules/things to move around.
Conduction can only occur in solid things, like the ground.
The Atmosphere: Layers
The upper and lower regions of the atmosphere contain the same density of matter.
Solution
The lower regions are more dense because the weight of the particles above compacts the particles more below.
In which layer does weather and all the breathable air exist?
Solution
The order of the spheres and pauses from low to high are:
troposphere ↔ tropopause ↔ stratosphere ↔ stratopause ↔ mesosphere ↔ mesopause ↔ thermosphere.
Weather and air are only located within the troposphere.
(It is important to protect this thin layer of the atmosphere to preserve life)
troposphere ↔ tropopause ↔ stratosphere ↔ stratopause ↔ mesosphere ↔ mesopause ↔ thermosphere.
Weather and air are only located within the troposphere.
(It is important to protect this thin layer of the atmosphere to preserve life)
The Ozone Layer is located within which region of the atmosphere?
Solution
The ozone (O3) that protects life from harmful radiation from the Sun is located in the Stratopause.
Which of the following layers can reach the coldest temperatures?
Solution
The order of the spheres and pauses from low to high are:
troposphere ↔ tropopause ↔ stratosphere ↔ stratopause ↔ mesosphere ↔ mesopause ↔ thermosphere.
The mesopause reaches the coldest temperatures. Many people (incorrectly) think it's the top layer.
troposphere ↔ tropopause ↔ stratosphere ↔ stratopause ↔ mesosphere ↔ mesopause ↔ thermosphere.
The mesopause reaches the coldest temperatures. Many people (incorrectly) think it's the top layer.
The Atmosphere: Lapse Rate
Lapse rate is calculated by the change in air temperature divided by the change in height (or altitude)
Solution
True
In which region does lapse rate increase?
Solution
The lapse rate increases in the stratosphere and thermosphere. It decreases in the troposphere, and mesosphere. The order of the spheres and pauses from low to high are: troposphere ↔ tropopause ↔ stratosphere ↔ stratopause ↔ mesosphere ↔ mesopause ↔ thermosphere.
The Biosphere
Choose the best answer. The biosphere (all living organisms) can exist within the:
Solution
Life can be found below ground, living within the lithosphere. Life can also be found floating in the air (atmosphere) in small particles, or flying as larger animals. Life can also be found living in the water systems (hydrosphere).
Atmospheric Gases
Which of the following is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere?
Solution
Nitrogen at 79% !
The Earth's Spheres
A handful of soil can contain which of the following four spheres of earth?
Solution
In soil there can be: rock, water, air, and life.
 |
Clouds
Choose the best description. Clouds are formed when: Solution
 |
Clouds are part of the hydrosphere, and are made of water vapour.
Solution

It is true that clouds (water) is part of the hydrosphere (rather than the atmosphere). Actually the part of clouds we see are made up of droplets of water that have condensed from gaseous vapour into liquid form.
Water in Air
Cold air is denser than warm air, so cold air holds more water moisture than warm air.
Solution
Cold air holds less water than warm air. Water can evaporate more in warm air, and when this air cools some of the vapour condenses out of the air into the liquid phase.
Heat in the Hydrosphere and Atmosphere
One of the effects of heat transfer in the atmosphere and hydrosphere is the movement of water, known as the water cycle.
Solution
The phase changes of water in the water cycle are caused by heat (changes in temperature) from energy coming originally from the sun.
Convection
The movement of fluid (liquid and air) masses from regions of low to high pressure creates something called convection.
Solution
This is all true except one thing: that fluid (liquid and air) moves always from high to low pressure.
Climate Regions
The climate of a region in Southern Ontario, Canada would be most similar to a climate in another part of the world if which of the following are similar between the regions?
Solution
Climate, or "weather conditions" depends on a number of factors such as temperature, humidity, precipitation levels ... Regions in similar latitudes experience similar conditions.
Sources and Sinks
Which of the following is the main source of carbon in the atmosphere?
Solution
While some of the other answer choices do contribute to the carbon in the atmosphere the main source is outgassing and volcanoes.
Sources and Sinks
The only major carbon sink on Earth is photosynthesis.
Solution
The other main sink is ocean sedimentation of carbon-containing matter, such as shells and other biomass.
Carbon
Carbon can be absorbed from the air into the ocean.
Solution
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water in the gas form and forms aqueous carbonic acid H2CO3, bicarbonate HCO3-, and carbonate CO32-...
The Coriolis Effect
In the northern hemisphere, wind deflects to the left.
Solution
In the northern hemisphere, wind deflects to the right due to the Coriolis effect.
Describe the movement of the Trade winds in the Northern Hemisphere if the Earth did not rotate.
Solution
The rotation of the Earth causes the Coriolis effect, so if there was no Coriolis effect then the trade winds would not curve down and westbound, instead they would just go straight downwards.
Greenhouse Gases
Which of the following is not one of the most abundant greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere?
Solution
Diatomic gases X2 are not greenhouse gases because they do not vibrate when hit by infrared radiation. This is already more than you need to know for this course. (You don't need to know that diatomic gases don't vibrate because they are non-polar so they have no dipole moment.)
Greenhouse Gases
The greenhouse gas effect is a completely unnatural occurrence that will eventually ruin our environment.
Solution
Actually life on earth would not survive without the warmth that greenhouse gases provide. Greenhouse gases have been around and are almost as old as the Earth itself. However an important balance exists and if the anthropogenic ("manmade") greenhouse effect gets too strong, then it could become dangerous.
Albedo
Which of the following does not contribute largely to the albedo effect of the Sun on the Earth? Solution
 |
Ice, snow, and clouds are main ones. Dry sand reflects more light than water. So water does not contribute largely to the albedo effect.
The Five Main Effects of Climate Change in the Atmosphere
Which of the following are not one of the five main effects of climate change in the atmosphere?
Solution
Five main effects of climate change in the atmosphere:
- Heat waves
- Drought
- Wildfires
- Storms
- Floods
- Heat waves
- Drought
- Wildfires
- Storms
- Floods
Effect of Climate Change in the Hydrosphere
Describe any two of the three main effects of climate change in the hydrosphere.
Solution
[Answers may vary] Describe: Melting ice, ocean warming, and ocean currents. E.g. Warming water causes more hurricanes and storms, it decreases the gasses dissolved releasing greenhouse gases, and the warm water decreases the oxygen content dissolved for the aquatic life...
 |
Salt and Fresh Water
Which of the following bodies of water would be most dense?
Solution
Colder, saltwater is densest...
Flashcards: Earth and Space
| What does anthropogenic mean |
| Something cause by human activity (like increase of greenhouse gases) |
| Can convection occur in a liquid or a gas? |
| Yes |
| What is the only form of energy transfer that can occur in space? |
| Radiation |
| How does the density of the upper atmosphere compare the density of the lower atmosphere? |
| The density of the upper atmosphere is lower than the lower atmosphere |
| Which layer of the atmosphere contains the Ozone layer? |
| Stratopause |
| The change in air temperature divided by the change in altitude is what calculation? |
| Lapse rate |
| Lapse rate decreases in what 2 layers of the atmosphere? |
| Troposphere and mesosphere |
| In which layer does weather and all the breathable air exist? |
| Troposphere |
| Clouds are what sphere? |
| Hydrosphere (And contained within the atmosphere) |
| What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere? |
| Nitrogen |
| How do clouds form? |
| Water vapour condenses as moist air masses rise and cool. |
| Convection always moves a fluid in what direction? |
| From high to low pressure |
| What causes the trade winds in the northern hemisphere? |
| The Coriolis effect (from the rotation of the Earth) |
| Is water vapor a greenhouse gas? |
| Yes |
| What is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere? |
| Water vapor |
| What is albedo? |
| The proportion of the reflection of incident light on a surface |
Physics: Light and Geometric Optics
Light as Energy
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet light in the visible spectrum are all forms of energy.
Solution
True. The visible region of electromagnetic radiation is abbreviated as wavelengths: R-O-Y-G-B-I-V
Light Waves
Electromagnetic waves can travel in a vacuum.
Solution
True. This is why light energy can travel through the vacuum of space from our Sun to our Earth.
Electromagnetic Waves
Rank the following wavelengths in order of decreasing energy (top to bottom).
Solution
Visible
Ultraviolet
Radio
Gamma
Microwave
Order: Gamma, Ultraviolet, Visible, Microwave, Radio.
This is considered basic, required knowledge for your class this year.
Sources of Light
Of all the things listed below that you can see when light comes from them, which of the following is considered luminous?
Solution
Luminous sources produce their own light, like fire. Whereas metal, diamond, glass, and water only reflect light from other sources, rather than producing light.
Types of Light Production
Light that is emitted due to high temperatures is called
Solution
Incandescence is not the most efficient form of light production. This is due to considerable amounts of heat energy lost...
Types of Light Production
Lightning and neon signs produce light through a process known as __________. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Electric discharge is the production of light when electric current flows through a gas (air, or noble gas) and causes the gas to glow. The natural example of this is lightning. Neon signs and fluorescent lamps use electric discharge - electricity flows through various gases to produce light. Fluorescent lamps require one extra step to make the light visible to us.
Types of Light Production
The generation of light through mechanical means by scratching, crushing, rubbing, or pulling apart is called:
Solution
Triboluminescence is cool. It can be observed when quartz rocks are shaken vigorously in a dark environment.
Types of Light Production
One example of phosphorescence is the light emitted from glow-in-the-dark pigments.
Solution
Phosphorescence pigments (phosphor) absorb light energy (often spectrums we cannot see, e.g. ultraviolet light) and store and release this energy for a certain amount of time.
An other example of phosphorescence is night vision goggles, check it out:
An other example of phosphorescence is night vision goggles, check it out:
Types of Light Production
Fluorescent lights contain a gas that converts electric current to ultraviolet light by a process known as electric discharge. Explain what happens to this ultraviolet light next, since this is not yet useful as visible light. [3]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Fluorescent light bulbs must be coated in a fluorescent material that converts ultraviolet light to visible light.
Electric current provides the energy that excites electrons in Mercury atoms. When these electrons in the Mercury atoms transition, or change back, light is emitted in the ultraviolet spectrum that we cannot see. This ultraviolet light then excites a fluorescent pigment (phosphor) coating around the bulb, that converts the ultraviolet light to light in the visible spectrum that we can see.
Electric current provides the energy that excites electrons in Mercury atoms. When these electrons in the Mercury atoms transition, or change back, light is emitted in the ultraviolet spectrum that we cannot see. This ultraviolet light then excites a fluorescent pigment (phosphor) coating around the bulb, that converts the ultraviolet light to light in the visible spectrum that we can see.
Types of Light Production
Describe the main difference between fluorescence and incandescence. [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Fluorescence uses electric discharge to create ultraviolet light that gets converted to visible light. Incandescence heats up a material that emits visible light.
What is bioluminescence? [1] Solution
 |
Some bioluminescent organisms: works, flies, fish, fungi, bacteria...
Light Transmission
Opaque surfaces do not allow any light to pass through them. Translucent surfaces allow some light to pass while blocking some details.
Solution
True...
Which of the following materials is transparent?
Solution
Water is transparent. Transparent things allow light to pass through completely.
The Law of Reflection
State the law(s) of reflection in your own words. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The angle of incidence (θi) of a light ray is equal to the angle of reflection (θr). Both angles are measured from the normal, which is a perpendicular line of reference from the surface of the mirror. The incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
Plane Mirrors
Images in plane mirrors are real.
Solution
Images in plane mirrors are virtual.
Terminology: LOST or SALT
Different curriculums use different acronyms to describe the characteristics of an image. Define the acronym used by your class below.
The acronym, LOST stands for:
Solution
Describes the characteristics of an image
- Location = Relative to center of lens or focus f/f'
- Orientation = Upright/Inverted
- Size = Magnified/Smaller
- Type = Real/Virtual
- Location = Relative to center of lens or focus f/f'
- Orientation = Upright/Inverted
- Size = Magnified/Smaller
- Type = Real/Virtual
The acronym, SALT (less common form of LOST) stands for:
Solution
Describes the characteristics of an image
- Size = Magnified/Smaller
- Attitude = Upright/Inverted
- Location = Relative to center of lens or focus f/f'
- Type = Real/Virtual
- Size = Magnified/Smaller
- Attitude = Upright/Inverted
- Location = Relative to center of lens or focus f/f'
- Type = Real/Virtual
Converging (Concave) Mirrors
A concave mirror will produce an upright image if the object is:
Solution
In front of the focal point
Converging (Concave) Mirrors: Object > C
Determine the SALT/LOST characteristics of the image formed when the object is outside the centre of curvature, C.
Solution



Converging (Concave) Mirrors: Object = C
Determine the characteristics of the image formed when the object is located at the centre of curvature, C.
Solution



Converging (Concave) Mirrors: Object < C
Determine the characteristics of the image formed when the object is located inside the centre of curvature, C.
Solution



Converging (Concave) Mirrors: Object = F
Determine the characteristics of the image formed when the object is located at the focus, F.
Solution



Converging (Concave) Mirrors: Object < F
Determine the characteristics of the image formed when the object is located inside the focus, F.
Solution



Images: Real and Virtual
What is the main difference between a real and virtual image? [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Real images form on the same side of the mirror that the light goes to. Virtual images form on the side of the mirror that the light cannot go to.
Diverging (Convex) Mirrors
A diverging (convex) mirror always produces a smaller, upright, virtual image, behind the mirror.
Solution
Convex mirrors never produce real images.
Diverging (Convex) Mirrors
Determine the characteristics of the image formed.
Solution



Refraction
Explain the cause of refraction. [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Refraction occurs when the transmission of light across a boundary between two media of different densities is accompanied by a change in the speed, and wavelength of the wave.
For example, when the light slows down, the wavelength decreases. This causes the light wave to 'bend' away from the normal, increasing the angle of refraction.
The angle of refraction depends on the initial angle of incidence, and if the angle of incidence is parallel to the normal then the light does not refract.
For example, when the light slows down, the wavelength decreases. This causes the light wave to 'bend' away from the normal, increasing the angle of refraction.
The angle of refraction depends on the initial angle of incidence, and if the angle of incidence is parallel to the normal then the light does not refract.
State the first law of refraction. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
State the second law of refraction. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
(Snell's and Descartes' Law)
θi is the angle of incidence
θr is the angle of refraction
ni is the index of refraction of the incident medium
nr is the index of refraction of the refractive medium
θi is the angle of incidence
θr is the angle of refraction
ni is the index of refraction of the incident medium
nr is the index of refraction of the refractive medium
What is one use/application of refraction? [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
E.G.) Glasses and contact lenses refract the path of light to correct near-sighted or far-sighted vision.
Refraction
Describe an example in which you can see reflection and refraction occur at the same time. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
On a dark night, when you look outside a window and see your own reflection, at the same time refraction is occurring from the light traveling from the bright room to the outside.
Or during the day, seeing your reflection in the water at the same time as seeing anything under the water surface.
(Accept anything else in which reflection and refraction occur at the same time)...
Or during the day, seeing your reflection in the water at the same time as seeing anything under the water surface.
(Accept anything else in which reflection and refraction occur at the same time)...
Refraction
As light enters a denser medium, the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence.
Solution
As light enters a denser medium, the angle of refraction is less than the angle of incidence.
Refraction
You see a quarter at the bottom of your swimming pool and decide to get it. Compared to what you see, you should reach:
Solution

The quarter appears farther (dashed white line) than it actually is.
Refraction
Objects under water always appear closer to the surface than they actually are.
Solution
True. This is due to the angle of refraction of the light traveling from the object underwater to the observer above. While the light observed is the refracted light, the eyes and brain imagine the light in a completely straight path without refraction. So you see the image larger, while the brain thinks it is further. This makes it appear closer or larger.
Rainbow Formation
Explain how a rainbow forms. What type of image is it? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Light is refracted by liquid water droplets suspended in the air as it first enters the water drop. Sunlight is white light that is actually made up of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet light. Each colour has a slightly different wavelength, so each colour bends or refracts at slightly different angles. The light is partially internally reflected off the inside of the water drop, gets split up into a spectrum, and refracts again as it exits. To see a rainbow, you have to be standing with the sun behind you. Red light is seen at the top from a water drop higher up above, while violet light is seen at the bottom of the rainbow. A rainbow is a virtual image.


Mirages
What causes the water-like shimmer above a road or desert, called a mirage? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Cold, dense air has a greater index of refraction, n than warmer air. As light travels from cold air to hot air (closer to the ground), the light bends in an arc upwards. The eye interprets the light rays to have been straight, which makes the blue light - that was originally from the sky - look as if it came from the ground. This causes the bluish shimmer of a mirage to appear like water at or below ground level.
Labelling Refraction Diagrams
Which is the location of the angle of refraction?
Solution

The angle of refraction is measured from the normal to the refracted ray, iii.
Speed of Light
The speed of light in a vacuum is
Solution
The speed of light in a vacuum is constant everywhere in the universe...3.0 × 108m/s
Index of Refraction Equation
Index of refraction, n is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum, c to the speed of light in a particular medium, v.
Solution
True.
Index of refraction is calculated by dividing the speed of light in a vacuum, c to the speed of light in a particular medium, v. The speed of light is fastest in a vacuum (like space) is constant, always 3.0 × 108 m/s. The speed of light slows down in other mediums like air or water. When you divide the two you get the ratio, n called the index of refraction.
n = c / v
Maybe you can tell that this ratio will always be greater than 1.0 !
Index of refraction is calculated by dividing the speed of light in a vacuum, c to the speed of light in a particular medium, v. The speed of light is fastest in a vacuum (like space) is constant, always 3.0 × 108 m/s. The speed of light slows down in other mediums like air or water. When you divide the two you get the ratio, n called the index of refraction. n = c / v Maybe you can tell that this ratio will always be greater than 1.0 !
Explain why the index of refraction, n is always greater than one. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Since the speed of light is always faster in a vacuum (c) than in any medium (v), then dividing,
... will always be greater than one because the numerator will always be greater than the denominator in the equation shown.
Index of Refraction
When the speed of refracted light increases, it bends towards the normal.
Solution
In a faster, less dense medium, when the speed of refracted light increases, it bends away from the normal.
Index of Refraction
Emerald has an index of refraction of 1.6, and if light can travel in a ruby at 1.695 × 108 m/s, in which medium can light travel faster? [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Light travels faster in emerald.
Light travels faster in emerald.
Index of Refraction
Which of the following would refract light the most? Solution
| Medium | Index of Refraction (n) |
| Air | 1.00 |
| Water | 1.33 |
| Olive oil | 1.48 |
| Glass | 1.52 |
| Diamond | 2.42 |
Index of Refraction
The speed of light in an unknown medium is calculated as 2.03 × 108 m/s. Determine the identity of the unknown medium. Solution
| Medium | Index of Refraction (n) |
| Air | 1.00 |
| Water | 1.33 |
| Olive oil | 1.48 |
| Glass | 1.52 |
| Diamond | 2.42 |
You need to know, and use the speed of light: c = 3.0 × 108m/s.
Total Internal Reflection
Total internal reflection occurs if the angle of incidence is less than the critical angle.
Solution
Total internal reflection occurs if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. Also, light must travel from a medium with a higher index of refraction (n) to a medium with a lower index of refraction (n).
Total Internal Reflection
If the critical angle of a certain material is 25˚, which angle of incidence would cause total internal reflection?
Solution
Total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence is greater than or equal to the critical angle.
θi ≥ θc
Note that a 90˚ angle of incidence would be parallel to the plane of the surface and would neither reflect nor refract.
(It is not possible for the angle of incidence to be greater than 90˚).
(It is not possible for the angle of incidence to be greater than 90˚).
Total Internal Reflection
What two conditions are necessary for total internal reflection to occur? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
1) Light rays must have an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle for a particular medium.
2) light must travel from a slower (denser, higher refractive index, n) medium to a faster (less dense, lower refractive index, n).
For example, this could occur with light travelling from diamond (2.4) to air (1.00) but not from air to diamond.
2) light must travel from a slower (denser, higher refractive index, n) medium to a faster (less dense, lower refractive index, n).
For example, this could occur with light travelling from diamond (2.4) to air (1.00) but not from air to diamond.
What is one useful, major technological application of total internal reflection? Explain how this works. [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Fiber optic cables transmit information at the speed of light through fiber optic cables made out of silica glass or plastic which has a low critical angle causing the light rays to reflect inside the cable resulting in total internal reflection. It is important for the core of the cables to have a higher index of refraction than the surrounding material for the light to be totally internally reflected. Fiber optic cables can stretch over longer distances than traditional metal cables, and can also support higher bandwidth usage. Other things that use total internal reflection: binoculars, and periscopes. [Answers may vary]
Critical Angle
Determine the critical angle of light that travels from ice (n = 1.3) to air (n = 1).
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
degrees
Hint Unavailable
n1 is the medium that the light originates from, n2 the other...
Starting index medium, n1 = 1.3
Second index medium, n2 = 1.0

Starting index medium, n1 = 1.3 Second index medium, n2 = 1.0

Detail Comparing the Principle Focus (F not F') of a Convex and Concave Lens
The principle focus is the point where light rays converge from a lens. The principle focus on a converging lens is located on the __________ side, and the principle focus on a diverging lens is located on the __________ side.
Solution
Converging (convex) lenses have the focus on the real side -- the side that the light travels to. Diverging (concave) lenses have the focus on the virtual side -- the side the light does not go to.
Converging (Convex) Lens
Complete the following table (in your own notes) for a converging lens. Solution
 |
| Object Location: | Object > 2F' | Object at 2F' | 2F' < Object < F' | Object = F' | Object < F' |
| Size: | |||||
| Attitude (Orientation): | |||||
| Location: | |||||
| Type: |
| Object Location: | Object > 2F' | Object at 2F' | 2F' < Object < F' | Object = F' | Object < F' |
| Size: | Smaller | Same | Larger | No Image | Larger |
| Attitude (Orientation): | Inverted | Inverted | Inverted | No Image | Upright |
| Location: | 2F > Object > F | Object = 2F | Object > 2F | No Image | Image > F' |
| Type: | Real | Real | Real | No Image | Virtual |

As the object distance increases from a converging lens...
Solution
As the object is moved further away from the converging lens, the image formed gets smaller and the image becomes closer to the lens. (If the object is infinitely far from the lens, then the image is infinitely small. There is only no image formed when the object is at the focus, F'.)


For a converging lens, an image never forms when the object is located at F'.
Solution
The parallel ray and the center ray will refract in the lens to produce parallel rays, which will never converge, thus no image will ever form.


When is the only time a converging lens will produce an upright, virtual image.
Solution
When the object is located < F' (between the focus and the lens)


Converging (Convex) Lens
For a converging lens...
Determine the 4 SALT characteristics when an object distance is less than the focal (F') distance.
Solution
The image is: magnified, upright, >F', and virtual.

CC: Durova, 2009
 |
An object located at the focus, 'f' will...
Solution
The parallel (p) and center (c) rays will refract through the lens and never converge, and therefore an image is never formed.


Diverging (Concave) Lens
Complete the following table for a diverging lens Solution
 |
| Object Location: | Object > 2F | Object at 2F | 2F < Object < F | Object < F |
| Size: | ||||
| Attitude (Orientation): | ||||
| Location: | ||||
| Type: |
| Object Location: | Object > 2F | Object at 2F | 2F < Object < F | Object < F |
| Size: | Smaller | Smaller | Smaller | Smaller |
| Attitude (Orientation): | Upright | Upright | Upright | Upright |
| Location: | Image < F' | Image < F' | Image < F' | Image < F' |
| Type: | Virtual | Virtual | Virtual | Virtual |
A concave lens will always produce a smaller image.
Solution
The size of the image is always smaller.
A diverging lens always produces an inverted image.
Solution
The attitude (orientation) of the image is always upright.
Converging and Diverging Lens Images
Real images are always inverted. Virtual images are always upright.
Solution
True. Real images are always inverted. Virtual images are always upright.
Diverging (Concave) Lens
A diverging lens never produces a real or inverted image. Solution
 |
The image is always upright.
The image formed by a diverging (concave) lens is always upright, virtual, and smaller than the object.
Solution
Diverging, concave lenses produce virtual images, never real images.
The parallel ray from the object will appear to refract...
Solution
The parallel ray will refract and diverge on the real side. On the virtual side, the ray will appear to pass through the focus (f').
(Math Review) Order of Operations
Solve for 'd' algebraically.
Solution
d =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The Mirror/Lens Equation
Remember the following rules when using the lens equation.
- do is always positive.
- di is positive for real images, and negative for virtual images.
- f is positive for converging (convex) lenses, and negative for diverging (concave) lenses.
An object is located 20 cm from a converging mirror or lens with a focal length of 10 cm. Determine the type of image formed.
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
image
Hint Unavailable
+ di = real
- di = virtual...
f = 10cm, do = 20cm.
Positive image distance (+20 cm), therefore the image formed is real (as opposed to virtual that would have a negative image distance).
- di = virtual...
f = 10cm, do = 20cm.
Positive image distance (+20 cm), therefore the image formed is real (as opposed to virtual that would have a negative image distance).
A converging lens forms a virtual image 50 cm from the mirror or lens, which has a focal length of 25 cm. Determine the distance between the object and the optical center.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
cm
Hint Unavailable
di is negative for virtual images.
di = -50cm, f = 25cm.
di = -50cm, f = 25cm.
A diverging mirror or lens has a focal length of 44 cm and forms a virtual image 12 cm from the optical center. Determine the distance between the object and the optical center.
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
cm
Hint Unavailable
di is negative for virtual images.
f is negative for diverging (concave) lenses.
di = -12cm, f = -44cm.
f is negative for diverging (concave) lenses.
di = -12cm, f = -44cm.
The Magnification Equation for Mirrors or Lenses
Remember the following rules when using the magnification equation.
- ho and hi (height) are positive when upright, and negative when inverted.
- do (distance) is always positive.
- di (distance) is positive for real images, and negative for virtual images.
- M (magnification) is positive for upright images, and negative for inverted images.
A converging mirror or lens produces a real, inverted image 15 cm in height. If the object is 30 cm in height, determine the magnification of the mirror or lens.
Solution
M =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
hi = -15cm (negative for inverted), ho = 30cm.
The magnification is smaller (0.5), and inverted because it is negative.
The magnification is smaller (0.5), and inverted because it is negative.
A converging mirror or lens produces a virtual, upright image 10 cm from the optical center. If the object is situated 5 cm from the mirror or lens, determine the magnification.
Solution
M =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
di = -10cm (negative for virtual image), do = 5cm.
A converging mirror or lens produces a real, inverted image 40 cm from the optical center. If the object is situated 40 cm from the mirror or lens, determine the magnification.
Solution
M =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
di = 40cm, do = +40cm.
An object is situated 10 cm in-front of a converging mirror or lens, which produces a real, inverted image that is magnified by a factor of -2.5. Determine the distance between the image and the optical center.
Solution
di =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
cm
Hint Unavailable
M = -2.5 (negative M means inverted), do = +10cm.
(Since the image distance is positive, the image is real)
(Since the image distance is positive, the image is real)
A diverging mirror or lens produces a virtual, upright image 12 cm from the optical center. If the object is situated 50 cm from the mirror or lens, determine the magnification of the lens.
Solution
M =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
di = -12cm (negative because image is virtual), do = +50cm.
An inverted object is 10 cm in height with a converging mirror or lens, if the image is magnified by a factor of -1.75, determine the height of the image.
Solution
hi =
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
cm
Hint Unavailable
M = -1.75, ho = -10cm (negative because inverted).
The Magnification Equation
A converging lens has a focal length of 15 cm, and if an object is placed 20 cm from the center, calculate the magnification of the image, and determine the attitude (orientation) of the image. [2]
Solution
Video
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Use the lens equation to find the image distance.
Use the magnification equation
The image is inverted (because negative M), and larger (because absolute value |M| is greater than 1).


Lens Technology
Fill in the blanks for the size of the image produced by a magnifying glass, and the type of image formed by a microscope. Solution
| Device | Lenses Used | Size | Attitude | Location (Image) | Type |
| Magnifying Glass | Converging | _________ | Upright | Between Lens and F' | Virtual |
| Camera | Converging | Smaller | Inverted | Between F and 2F | Real |
| Microscope | 2 Converging | Larger | Inverted | Final image located >>> F' | _________ |
| Telescope | 2 Converging | Larger | Inverted | Final image >>> F' | Virtual |
(A microscope and telescope will produce an image much farther than the virtual focal, f' distance, with respect to the final eyepiece lens)
A magnifying glass will always produce a larger, upright, virtual image. (Determine which diagram is used in a magnifying glass setup.)
Solution
A magnifying glass only works with the setup on the bottom, where the object is located between the lens and the (virtual, f') focal point. (The magnifying glass won't work properly if the object distance is greater than or equal to the focal distance.)

In simple light microscopes and astronomical telescopes, the objective lens produces an inverted, real image. The eyepiece lens produces an upright, virtual image.
Solution
True.
 |
Chromatic Aberration
Chromatic aberration can be seen when a lens fails to converge the different colors of light at the same point.
What causes chromatic aberration?
Solution
When the different wavelengths of light refract at different angles and focus at different distances, fringes of light (mainly red, 650nm and blue, 450nm) are seen at the edges of images.

CC: Stan Zurek, 2006
 |
What is chromatic aberration and what is used to correct it? [2]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Chromatic aberration is the refraction of different wavelengths of light (red, green, blue) at different angles:

CC: Bob Mellish, 2006
Chromatic aberration is corrected with an achromatic doublet. The first lens is called the crown lens (convex), and the second is called the flint (concave). The flint is used to bring the red and blue wavelengths into focus (achromatic). Bringing into focus means causing the rays to convert at the same point.

CC: Bob Mellish, 2006
 |
 |
Lens Technology
What type of lenses do you think are used in binoculars? [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Achromatic doublet lenses (which are based on converging lenses):

CC: Antilived, 2006
 |
What type of device does this lens diagram depict? [1]
Solution
 Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
This is a Galilean telescope.
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
This is a Galilean telescope.
The eyepiece is a diverging concave lens, and the objective is a converging convex lens.
(You can see the image formed, B is: magnified, upright, virtual.
The eyepiece is a diverging concave lens, and the objective is a converging convex lens.
(You can see the image formed, B is: magnified, upright, virtual.
What type of device does this lens diagram depict? [1] Solution
 |
The eyepiece (not shown here), objective, and condenser lenses are all converging, convex lenses.
How it works... The objective lens magnifies the image first. Then the eyepiece lens takes this image and magnifies it much more into a much larger, second image. This final image is many times larger than the original object and is a virtual image.
Astronomical telescopes and light microscopes both use 2 converging lenses.
Solution
True. They both use one objective lens and one eyepiece lens - both are converging lenses. In both cases the eyepiece does most of the magnification, and both final images in the eyepieces are inverted and virtual (the first image in the objective is inverted and real).
One of the main differences is the astronomical telescope will have a much greater object distance.
One of the main differences is the astronomical telescope will have a much greater object distance.
The Eye
Label the missing names.
Solution



On what part of the eye is the image formed (where light is detected)?
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The image is formed on the retina, located at the back of the eyeball.
What part of the eye regulates the light input?
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
The iris.
What type of lens is in the eye? [1]
Solution
Hint
Clear
Info
Incorrect Attempts:
CHECK
Hint Unavailable
Converging, convex lens.
The Eye
The image produced by the eye is smaller, upright, and real
Solution
The image produced by the eye is smaller, inverted, and real
Problems With Focusing (Accommodation)
When the eye produces an image in-front of the retina, this is called
Solution
Myopia, or Nearsightness

A shortsighted/nearsighted (myopic) person can see
Solution
Shortsighted/nearsighted (myopic) people can only see objects clearly that are close to the lens because the light rays are not parallel but are more divergent and will converge further back on the retina when the object is closer. The image must converge precisely on the retina to be seen clearly.

CC, A. Baris Toprak MD, 2007
 |
Presbyopia and Hyperopia are both forms of nearsightedness
Solution
Presbyopia and Hyperopia are both forms of Far-Sightedness.
(Presbyopia is caused by a lack of elasticity of the eye due to old age.)

CC, A. Baris Toprak MD, 2007
 |
Problems With Focusing (Accommodation)
Determine the types of lenses used to correct Hyperopia and Myopia Solution
| Common Name | Lens Used for Correction | |
| Hyperopia: | Farsighted | _______I________ |
| Myopia: | Nearsighted | _______II________ |
| Common Name | Lens Used for Correction | |
| Hyperopia: | Farsighted | Converging (Convex) |
| Myopia: | Nearsighted | Diverging (Concave) |
Hyperopia:
 |
 |
Flashcards: Physics
| What is the visible spectrum? |
| The region of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be detected with the human eye. (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet) |
| What is an electromagnetic wave? |
| Light |
| What is incandescence? |
| Light that is emitted due to high temperatures |
| What is a common example of electric discharge? |
| Lightning, or neon signs |
| What is electric discharge? |
| Electric discharge, which is the production of light when electric current flows through a gas (air, or noble gas) and causes the gas to glow. |
| What is triboluminescence? |
| The generation of light through mechanical means by scratching, crushing, rubbing, or pulling apart |
| What is phosphorescence? |
| Phosphorescence is the light emitted from glow-in-the-dark pigments, which is a way of storing energy as potential energy of electrons and then slowly emitting this light energy over time. |
| What is fluorescence? |
| Fluorescent lights contain a gas that converts electric current to ultraviolet light by a process known as electric discharge. Then the special fluorescent coating on the bulb converts this ultraviolet light to visible light. |
| Describe the main difference between fluorescence and incandesence |
| Fluorescence uses electric discharge to create ultraviolet light that gets converted to visible light. Incandescence heats up a material that emits visible light. |
| What is an opaque surface? |
| Opaque surfaces do not allow any light to pass through them |
| What is a translucent surface? |
| Translucent surfaces allow some light to pass while blocking some details |
| What is a transparent surface? |
| Transparent surfaces allow most light to pass with visual clarity |
| State the law of reflection |
| The angle of incidence (θi) of a light ray is equal to the angle of reflection (θr). |
| What is the difference between a real and virtual image? |
| A real image is formed on the side that light can physically go, while a virtual image is formed on the side where light cannot go |
| What does the acronym SALT stand for? |
| Size, Attitude, Location, Type |
| Does a diverging (convex) mirror always produces a virtual image? |
| Yes |
| If an image is located behind a mirror, what type of image is it? |
| Virtual |
| A virtual image has a ________ image distance |
| Negative |
| What type of image is formed when an object is placed inside the focal distance of a concave (converging) mirror. |
| Virtual, upright |
| What type of image is formed when an object is placed beyond the focal distance of a concave (converging) mirror. |
| Real, inverted |
| What is the difference in focal length of a concave (converging) mirror versus a convex (diverging) mirror |
| A concave (converging) mirror uses a positive focal length while a convex (diverging) mirror uses a negative focal length |
| What two processes occur in a raindrop that causes rainbows to form? |
| Refraction and total internal reflection |
| What is index of refraction (n)? |
| Index of refraction (n) is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum (c) to the speed of light in a particular medium (v). |
| When does total internal reflection occur? |
| Total internal reflection occurs for light starting inside a medium if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. Also, light must travel from a medium with a higher index of refraction (n) to a medium with a lower index of refraction (n) |
| What is a principle focus? |
| The principle focus is the point where light rays converge from a lens |
| What is the magnification of an image that is a greater distance than the object distance? |
| Larger |
| Can a concave (diverging) lens produce a real image? |
| No |
| What is the difference in focal length in converging (convex) lenses versus diverging (concave) lenses |
| Focal length (f) is positive for converging (convex) images, and negative for diverging (concave) images. |
| What is the difference in the height of an image (hi) and object (ho)? |
| ho and hi are positive for upright, and negative for inverted. |
| Can the object distance (do) ever be negative? |
| No, do is always positive |
| How is focal length (f) related to radius of curvature (r)? |
| Radius = 2(focal length) |
| State the first law of refraction |
| The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane |
| State the second law of refraction (Snell's law) |
| What happens to the speed of light as it crosses a boundary into a less dense medium |
| The light travels faster in a less dense medium |
| What happens to the angle of refraction of light as it crosses a boundary into a less dense medium |
| The light bends away from the normal |
| What is this value? 3.0 × 108 m/s |
| The speed of light in a vacuum (c) |
Scientific Investigation and Exploration
The Relationship Between Scientific Ideas, Hypothesis, and Data
Which of the following would be an effective way to help show the occurrence of global warming?
Solution
A good study will use the data over many years like the graph of average of the daily temperature data around the world for the past 100 years. This is a visual representation of the numeric data collected over as long a time span as possible for reliable data collection. The more data the better. Also a combination of many of the other data collections would be useful.
Formulating a Hypothesis Vs. Facts and Issues
Which of the following would be a hypothesis for the issue regarding: the use of solar and wind energy, instead of burning fossil fuels (oil, gas, etc.)?
Solution
A hypothesis is a proposition or explanation made without knowing the truth of it yet. This is posed as a statement (rather than as a question) and forms the basis for the research or questions that will be the scientific investigation to follow.
Selecting Appropriate Equipment and Materials for Scientific Inquires
A student wishes to measure the effects of acid rain on their local pond near a field. What item would be most necessary to include in this student's toolkit in the field?
Solution
The student must first check if the pond is acidic or not. This is done with pH paper.
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS)
Which of the following is WHMIS not used for?
Solution
The WHMIS book contains information on:
- Product information, including manufacturer and contact information
- Hazards, toxicology, and safety data
- Physical properties
- Etc...
- Product information, including manufacturer and contact information
- Hazards, toxicology, and safety data
- Physical properties
- Etc...
Appropriate Handling and Disposal Techniques
At the end of a classroom experiment in which several different chemicals were combined into a cool bubbly-foamy reaction, there are some extra chemicals left over. What should be done with these extra leftover chemicals?
Solution
As a general guideline,
- Don't put unused chemicals back into their original container. (Unless specifically instructed to do so by your teacher.)
- Don't pour chemicals down the sink drain. (Unless specifically instructed to do so by your teacher.)
- Don't put chemicals in the garbage. (Unless specifically instructed to do so by your teacher.)
- Don't put unused chemicals back into their original container. (Unless specifically instructed to do so by your teacher.)
- Don't pour chemicals down the sink drain. (Unless specifically instructed to do so by your teacher.)
- Don't put chemicals in the garbage. (Unless specifically instructed to do so by your teacher.)
Safety Equipment
Which of the following pieces of safety equipment is not considered actually necessary?
Solution
Be careful! Always wear all your safety stuff in the chemistry lab! Gloves, Goggles, Protective clothing and shoes are the main protective methods in a lab. Sometimes even more protection is used depending on the experiment.
Gathering Data in a Lab
A student wants to compare how higher temperature allows more salt to dissolve in water. To record and organize the temperature and amount of salt properly, the student should Solution
_onder_de_microscoop_creativeCommons.jpg) |
Controlling Variables
A controlled experiment changes two or more variables at a time to determine a change in a dependent variable.
Solution
A controlled experiment only changes one independent variable at a time, and measures the change or effect on the dependent variable.
Dependent and Independent Variables
A dependent variable is one which
Solution
A dependent variable changes due to the change in another variable, which is known as the independent variable. For example time is the independent variable and concentration of a chemical is the dependent variable. On an x-y graph, the 'y' values is dependent on the 'x' value.
Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Which of the following is not a quantitative observation?
Solution
Qualitative Observations
Qualitative observations are based on descriptions from sensory information like: sight, smell, texture, colour, values like good or bad, etc.
Quantitative Observations
Quantitative observations are based on numerical data that can be measured like: length, weight, volume, time, area, speed, temperature, number, etc...
Qualitative observations are based on descriptions from sensory information like: sight, smell, texture, colour, values like good or bad, etc.
Quantitative Observations
Quantitative observations are based on numerical data that can be measured like: length, weight, volume, time, area, speed, temperature, number, etc...
